Sections
Section I: Genotype Summary
Genotypes called: 21 / 21
| Drugs | Gene |
Genotypes
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABCG2 ‡ |
|
|||||||
| CACNA1S † ‡ |
|
|||||||
| CFTR ‡ |
|
|||||||
| CYP2B6 † ‡ |
|
|||||||
|
|
CYP2C19 † ‡ |
|
||||||
|
|
CYP2C9 † ‡ |
|
||||||
|
|
CYP2D6 † |
|
||||||
| CYP3A4 † ‡ |
|
|||||||
| CYP3A5 † ‡ |
|
|||||||
| CYP4F2 † ‡ |
|
|||||||
| DPYD † |
|
|||||||
|
|
G6PD † ‡ |
|
||||||
| HLA-B † |
|
|||||||
|
|
IFNL3/4 ‡ |
|
||||||
|
|
MT-RNR1 † |
|
||||||
| NUDT15 † ‡ |
|
|||||||
| RYR1 † |
|
|||||||
|
|
SLCO1B1 † ‡ |
|
||||||
| TPMT † ‡ |
|
|||||||
|
|
UGT1A1 † ‡ |
|
||||||
| VKORC1 ‡ |
|
|||||||
Section II: Prescribing Recommendations
abacavir
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Alternate Drug
|
Genotype
Phenotype
*57:01 positive |
HLA-B: Significantly increased risk of abacavir hypersensitivity | Abacavir is not recommended | Strong |
|
Population: Alternate Drug
|
Genotype
Phenotype
*57:01 positive |
HLA-B*57:01-positive patients have a strongly increased risk of a hypersensitivity reaction to abacavir. 48% of the HLA-B*57:01-positive patients develop a severe and potentially life-threatening hypersensitivity reaction to abacavir |
Abacavir is contra-indicated for HLA-B*57:01-positive patients.
|
Unspecified |
|
Population: Alternate Drug
|
Genotype
Phenotype
*57:01 positive |
"All patients should be screened for the HLA-B*5701 allele prior to initiating therapy with ZIAGEN [abacavir] or reinitiation of therapy with ZIAGEN, unless patients have a previously documented HLA-B*5701 allele assessment...ZIAGEN [abacavir] is contraindicated in patients: who have the HLA-B*5701 allele." See label for more information. * | Unspecified | |
|
Affected subgroup: HLA-B*57:01 allele positive Alternate Drug
|
Genotype
Phenotype
*57:01 positive |
"Results in higher adverse reaction risk (hypersensitivity reactions). Do not use abacavir in patients positive for HLA-B*57:01." * | Unspecified |
Citations:
- Clinical pharmacogenetics implementation consortium guidelines for HLA-B genotype and abacavir dosing. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2012. PMID:22378157
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guidelines for HLA-B Genotype and Abacavir Dosing: 2014 update. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2014. PMID:24561393
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product ZIAGEN (abacavir sulfate), NDA020977, ViiV Healthcare Company.
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
acenocoumarol
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
-1639 GG |
The guideline does not provide a description of the impact of the -1639 GG genotype on acenocoumarol. | The guideline does not provide a recommendation for acenocoumarol in patients with the VKORC1 rs9923231 CC genotype (-1639 GG genotype). | No recommendation |
Citations:
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
allopurinol
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
*58:01 negative |
HLA-B: Low or reduced risk of allopurinol-induced SCAR | Use allopurinol per standard dosing guidelines | Strong | |
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Function |
The guideline does not provide a description of the impact of the ABCG2 rs2231142 GG genotype (c.421CC; p.141QQ) on allopurinol. | The guideline does not provide a recommendation for allopurinol in patients with the the ABCG2 rs2231142 GG genotype (c.421CC; p.141QQ) | No recommendation | |
|
FDA Label Annotation 1 |
Genotype
HLA-B:*15:02/*57:01
|
|
|||
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotype
HLA-B:*15:02/*57:01
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guidelines for human leukocyte antigen-B genotype and allopurinol dosing. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2013. PMID:23232549
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) guidelines for human leukocyte antigen B (HLA-B) genotype and allopurinol dosing: 2015 update. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2016. PMID:26094938
- Dutch pharmacogenetics working group guideline for the gene-drug interaction of ABCG2, HLA-B and Allopurinol, and MTHFR, folic acid and methotrexate. European journal of human genetics : EJHG. 2024. PMID:36056234
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product ALOPRIM (allopurinol), NDA020298, Mylan.
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
amitriptyline
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Dosing Info
|
Genotype
Phenotypes
Activity Scores
|
|
Consider a 25% reduction of recommended starting dose. Utilize therapeutic drug monitoring to guide dose adjustments.
Other ConsiderationsPatients may receive an initial low dose of a tricyclic, which is then increased over several days to the recommended steady-state dose. The starting dose in this guideline refers to the recommended steady-state dose. Dosing recommendations only apply to higher initial doses of TCAs for treatment of conditions such as depression. See other considerations for dosing recommendations for conditions where lower initial doses are used, such as neuropathic pain. |
Moderate |
|
Population: Dosing Info
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
The risk of side effects is increased, because the gene variation leads to higher plasma concentrations of the active metabolite nortriptyline and to a lesser extent of amitriptyline. | Use 75% of the standard dose and monitor the efficacy and side effects or the plasma concentrations of amitriptyline and nortriptyline to adjust the maintenance dose | Unspecified |
|
Affected subgroup: CYP2D6 ultrarapid, intermediate, or poor metabolizers No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
"May alter systemic concentrations." * | Unspecified |
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guideline for CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 genotypes and dosing of tricyclic antidepressants. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2013. PMID:23486447
- Clinical pharmacogenetics implementation consortium guideline (CPIC) for CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 genotypes and dosing of tricyclic antidepressants: 2016 update. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2017. PMID:27997040
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
amoxapine
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Affected subgroup: CYP2D6 ultrarapid, intermediate, or poor metabolizers No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
"May alter systemic concentrations." * | Unspecified |
Citations:
aripiprazole
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
The genetic variation increases the plasma concentration of the sum of aripiprazole and the active metabolite dehydroaripiprazole to a limited degree. There is insufficient evidence that this increases the risk of side effects. | NO action is needed for this gene-drug interaction. | Unspecified | |
|
FDA Label Annotation 1 |
Genotype
CYP2D6:*1/*3
|
|
|||
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotype
CYP2D6:*1/*3
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
- Dutch Pharmacogenetics Working Group (DPWG) guideline for the gene-drug interaction between CYP2D6, CYP3A4 and CYP1A2 and antipsychotics. European journal of human genetics : EJHG. 2024. PMID:37002327
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product ABILIFY (ARIPIPRAZOLE), NDA021436, Rebel Distributors Corp.
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product ABILIFY MAINTENA (aripiprazole), NDA202971, Otsuka America Pharmaceutical, Inc.
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product Abilify Asimtufii (Aripiprazole), Otsuka America Pharmaceutical, Inc - NDA217006/SUPPL-2, 01/22/2025.
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
atazanavir
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Other Guidance
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer |
UGT1A1: Reference UGT1A1 activity; very low likelihood of bilirubin-related discontinuation of atazanavir. |
There is no need to avoid prescribing of atazanavir based on UGT1A1 genetic test result. Inform the patient that some patients stop atazanavir because of jaundice (yellow eyes and skin), but that this patient’s genotype makes this unlikely (less than about a 1 in 20 chance of stopping atazanavir because of jaundice).
Other ConsiderationsAll studies correlating UGT1A1 genotypes with atazanavir adverse events have involved ritonavir boosting. However, concentration-time profiles are equivalent when boosted with either cobicistat or ritonavir (PMID 23532097), and bilirubin-related adverse events including discontinuation of atazanavir occur in a similar percentage of patients prescribed atazanavir with cobicistat or ritonavir (PMID 23532097). Associations between UGT1A1 genotype, bilirubin elevations, and atazanavir/r discontinuation therefore almost certainly translate to atazanavir/cobicistat. "reference" function refers to the UGT1A1 allele to which other alleles are compared. |
Strong |
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for UGT1A1 and Atazanavir Prescribing. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2016. PMID:26417955
atomoxetine
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Dosing Info
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
CYP2D6: Possibly higher atomoxetine concentrations as compared to normal metabolizers but questionable clinical significance. Intermediate metabolizers with an activity score of 1 may be at an increased risk of discontinuation as compared to poor metabolizers. |
Initiate with a dose of 40 mg/day and increase to 80 mg/day after 3 days. If no clinical response and in the absence of adverse events after 2 weeks, consider increasing dose to 100 mg/day. If no clinical response observed after 2 weeks, consider obtaining a peak plasma concentration (1 to 2 hours after dose administered). If <200 ng/mL, consider a proportional increase in dose to approach 400 ng/mL. Dosages greater than 100 mg/day may be needed to achieve target concentrations.
Other ConsiderationsTherapeutic range of 200 to 1000 ng/mL has been proposed (PMID 29493375). Limited data are available regarding the relationship between atomoxetine plasma concentrations and clinical response. Available information suggests that clinical response is greater in poor metabolizers (PMs) compared to non-PMs and may be related to the higher plasma concentrations 1 to 1.5 hours after dosing in PMs compared to non-PMs administered a similar dose. Furthermore, modest improvement in response, defined as reduction in ADHD-rating scale, is observed at peak concentrations greater than 400 ng/mL. Doses above 120 mg/day have not been evaluated. |
Moderate | |
|
Population: Dosing Info
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
CYP2D6: Possibly higher atomoxetine concentrations as compared to normal metabolizers but questionable clinical significance. Intermediate metabolizers with an activity score of 1 may be at an increased risk of discontinuation as compared to poor metabolizers. |
Initiate with a dose of 0.5 mg/kg/day and increase to 1.2 mg/kg/day after 3 days. If no clinical response and in the absence of adverse events after 2 weeks, consider obtaining a peak plasma concentration (1 to 2 hours after dose administered). If < 200 ng/mL, consider a proportional increase in dose to approach 400 ng/mL.
Other ConsiderationsTherapeutic range of 200 to 1000 ng/mL has been proposed (PMID 29493375). Limited data are available regarding the relationship between atomoxetine plasma concentrations and clinical response. Available information suggests that clinical response is greater in poor metabolizers (PMs) compared to non-PMs and may be related to the higher plasma concentrations 1 to 1.5 hours after dosing in PMs compared to non-PMs administered a similar dose. Furthermore, modest improvement in response, defined as reduction in ADHD-rating scale, is observed at peak concentrations greater than 400 ng/mL. |
Moderate | |
|
Population: Dosing Info
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
The dose requirement can be reduced, because the genetic variation results in a higher atomoxetine plasma concentration. | In the event of side effects occurring and/or a response later than 9 weeks: reduce the dose and check whether the effect is conserved The plasma concentration of atomoxetine is a factor of 2-3 times higher for IM than for NM at the same dose. | Unspecified | |
|
FDA Label Annotation 1 |
Genotype
CYP2D6:*1/*3
|
|
|||
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotype
CYP2D6:*1/*3
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline for Cytochrome P450 (CYP)2D6 Genotype and Atomoxetine Therapy. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2019. PMID:30801677
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
- Dutch pharmacogenetics working group (DPWG) guideline for the gene-drug interaction of CYP2D6 and COMT with atomoxetine and methylphenidate. European journal of human genetics : EJHG. 2023. PMID:36509836
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product Strattera (Atomoxetine hydrochloride), NDA021411, Eli Lilly and Company.
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
atorvastatin
In case no genotype can be determined, recommendations are based on the rs4149056 genotype alone as per guideline. The minor C allele at rs4149056 defines SLCO1B1*5.
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Function |
SLCO1B1: Typical myopathy risk and statin exposure |
Prescribe desired starting dose and adjust doses based on disease-specific guidelines.
Other ConsiderationsThe potential for drug-drug interactions and dose limits based on renal and hepatic function and ancestry should be evaluated prior to initiating a statin. |
Strong | |
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Function |
The guideline does not provide a description of the impact of the _SLCO1B1_ 521 TT genotype on atorvastatin. | The guideline does not provide a recommendation for atorvastatin in patients with the SLCO1B1 521 TT genotype | No recommendation | |
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotype
SLCO1B1:*1/*1
|
|
|||
Citations:
- The Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline for SLCO1B1, ABCG2, and CYP2C9 genotypes and Statin-Associated Musculoskeletal Symptoms. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2022. PMID:35152405
- Dutch Pharmacogenetics Working Group (DPWG) guideline for the gene-drug interaction between SLCO1B1 and statins and CYP2C9 and sulfonylureas. European journal of human genetics : EJHG. 2024. PMID:39676086
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
azathioprine
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotypes
|
|
Start with normal starting dose (e.g., 2-3 mg/kg/day) and adjust doses of azathioprine based on disease-specific guidelines. Allow 2 weeks to reach steady-state after each dose adjustment (PMID 20354201, 11302950, 15606506).
Other ConsiderationsNormal starting doses vary by race/ethnicity and treatment regimens. If standard dose is below normal recommended dose, dose reduction might not be recommended for intermediate metabolizers. |
Strong | |
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer |
The guideline does not provide a description of the impact of a normal metabolizer phenotype on azathioprine. | The guideline does not provide a recommendation for azathioprine in normal metabolizers | No recommendation | |
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer |
The guideline does not provide a description of the impact of a normal metabolizer phenotype on azathioprine. | The guideline does not provide a recommendation for azathioprine in normal metabolizers. | No recommendation | |
|
FDA Label Annotation 1 |
Genotypes
NUDT15:*1/*1;TPMT:*1/*1 |
|
|||
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotypes
NUDT15:*1/*1;TPMT:*1/*1 |
|
|||
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guidelines for thiopurine methyltransferase genotype and thiopurine dosing. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21270794
- Clinical pharmacogenetics implementation consortium guidelines for thiopurine methyltransferase genotype and thiopurine dosing: 2013 update. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2013. PMID:23422873
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline for Thiopurine Dosing Based on TPMT and NUDT15 Genotypes: 2018 Update. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2019. PMID:30447069
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product IMURAN (azathioprine), NDA016324, Sebela Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
brexpiprazole
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
There are indications supporting an increase in the exposure to brexpiprazole, but no indications supporting an increase in side effects in patients with this gene variation. | NO action is required for this gene-drug interaction. | Unspecified | |
|
FDA Label Annotation 1 |
Genotype
CYP2D6:*1/*3
|
|
|||
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotype
CYP2D6:*1/*3
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Dutch Pharmacogenetics Working Group (DPWG) guideline for the gene-drug interaction between CYP2D6, CYP3A4 and CYP1A2 and antipsychotics. European journal of human genetics : EJHG. 2024. PMID:37002327
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product REXULTI (brexpiprazole), NDA205422, Otsuka America Pharmaceutical, Inc.
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
capecitabine
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer Activity Score
2.0 |
DPYD: Normal DPD activity and "normal" risk for fluoropyrimidine toxicity | Based on genotype, there is no indication to change dose or therapy. Use label-recommended dosage and administration. | Strong | |
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
2.0 (Normal Metabolizer) |
The guideline does not provide a description of the impact of a DPYD activity score of 2 on capecitabine. | The guideline does not provide a recommendation for capecitabine in patients with a DPYD activity score of 2. | No recommendation | |
|
FDA Label Annotation 1 |
Genotype
DPYD:Reference/Reference
|
|
|||
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotype
DPYD:Reference/Reference
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guidelines for dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase genotype and fluoropyrimidine dosing. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2013. PMID:23988873
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for Dihydropyrimidine Dehydrogenase Genotype and Fluoropyrimidine Dosing: 2017 Update. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2018. PMID:29152729
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
- Dutch Pharmacogenetics Working Group (DPWG) guideline for the gene-drug interaction of DPYD and fluoropyrimidines. European journal of human genetics : EJHG. 2020. PMID:31745289
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product Xeloda (capecitabine), NDA020896, Genentech, Inc.
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
carbamazepine
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Alternate Drug
|
Genotype
Phenotype
*15:02 positive |
|
If patient is carbamazepine-naïve, do not use carbamazepine.
Other ConsiderationsOther aromatic anticonvulsants have weaker evidence linking SJS/TEN with the HLA-B*15:02 allele; however, caution should still be used in choosing an alternative agent. Previous tolerance of carbamazepine is not indicative of tolerance to other aromatic anticonvulsants. Aromatic anticonvulsants include carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, eslicarbazepine, lamotrigine, phenytoin, fosphenytoin, and phenobarbital. In addition to HLA-B*15:02, risk for carbamazepine-induced SJS/TEN has been reported in association with the most common B75 serotype alleles in Southeast Asia, HLA-B*15:08, HLA-B*15:11, and HLA-B*15:21. Although not described, the possibility of carbamazepine-induced SJS/TEN in association with less frequently carried B75 serotype alleles, such as HLA-B*15:30 and HLA-B*15:31, should also be considered. |
Strong |
|
Population: Other Guidance
|
Genotype
Phenotype
*15:02 positive |
|
The latency period for drug-induced SJS/TEN is short with continuous dosing and adherence to therapy (~4-28 days), and cases usually occur within three months of dosing; therefore, if the patient has previously used carbamazepine consistently for longer than three months without incidence of cutaneous adverse reactions, cautiously consider use of carbamazepine in the future.
Other ConsiderationsPrevious tolerance of carbamazepine is not indicative of tolerance to other aromatic anticonvulsants. Aromatic anticonvulsants include carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, eslicarbazepine, lamotrigine, phenytoin, fosphenytoin, and phenobarbital. In addition to HLA-B*15:02, risk for carbamazepine-induced SJS/TEN has been reported in association with the most common B75 serotype alleles in Southeast Asia, HLA-B*15:08, HLA-B*15:11, and HLA-B*15:21. Although not described, the possibility of carbamazepine-induced SJS/TEN in association with less frequently carried B75 serotype alleles, such as HLA-B*15:30 and HLA-B*15:31, should also be considered. |
Optional |
|
Population: Alternate Drug
|
Genotype
Phenotype
*15:02 positive |
|
If patient is carbamazepine-naïve, do not use carbamazepine.
Other ConsiderationsOther aromatic anticonvulsants have weaker evidence linking SJS/TEN with the HLA-B*15:02 allele; however, caution should still be used in choosing an alternative agent. Previous tolerance of carbamazepine is not indicative of tolerance to other aromatic anticonvulsants. Aromatic anticonvulsants include carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, eslicarbazepine, lamotrigine, phenytoin, fosphenytoin, and phenobarbital. In addition to HLA-B*15:02, risk for carbamazepine-induced SJS/TEN has been reported in association with the most common B75 serotype alleles in Southeast Asia, HLA-B*15:08, HLA-B*15:11, and HLA-B*15:21. Although not described, the possibility of carbamazepine-induced SJS/TEN in association with less frequently carried B75 serotype alleles, such as HLA-B*15:30 and HLA-B*15:31, should also be considered. |
Strong |
|
Population: Alternate Drug
|
Genotype
Phenotype
*15:02 positive |
The risk of carbamazepine-induced SJS/TEN is strongly increased the first three months in patients with the HLA-B*15:02 allele. The risk of carbamazepine-induced SJS/TEN in these patients is 1.8-7.7%. |
|
Unspecified |
|
Population: Alternate Drug
|
Genotype
Phenotype
*15:02 positive |
"Tegretol [carbamazepine] should not be used in patients positive for HLAB*1502 unless the benefits clearly outweigh the risks." See label for more information. * | Unspecified | |
|
Affected subgroup: HLA-B*15:02 allele positive Alternate Drug
|
Genotype
Phenotype
*15:02 positive |
"Results in higher adverse reaction risk (severe skin reactions). Avoid use unless potential benefits outweigh risks and consider risks of alternative therapies. Patients positive for HLA-B*15:02 may be at increased risk of severe skin reactions with other drugs that are associated with a risk of Stevens Johnson Syndrome/Toxic Epidermal necrolysis (SJS/TEN). Genotyping is not a substitute for clinical vigilance." * | Unspecified |
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guidelines for HLA-B genotype and carbamazepine dosing. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2013. PMID:23695185
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline for HLA Genotype and Use of Carbamazepine and Oxcarbazepine: 2017 Update. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2018. PMID:29392710
- Dutch Pharmacogenetics Working Group (DPWG) guideline for the gene-drug interaction of CYP2C9, HLA-A and HLA-B with anti-epileptic drugs. European journal of human genetics : EJHG. 2024. PMID:38570725
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product Tegretol (carbamazepine), NDA016608, REMEDYREPACK INC.
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
celecoxib
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer Activity Score
2.0 |
CYP2C9: Normal metabolism | Initiate therapy with recommended starting dose. In accordance with the prescribing information, use the lowest effective dosage for shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals. | Strong | |
|
FDA Label Annotation 1 |
Genotype
CYP2C9:*1/*1
|
|
|||
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotype
CYP2C9:*1/*1
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline (CPIC) for CYP2C9 and Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2020. PMID:32189324
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product CELEBREX (Celecoxib), NDA020998, Aphena Pharma Solutions - Tennessee, LLC.
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
citalopram
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer |
CYP2C19: Normal metabolism | Initiate therapy with recommended starting dose | Strong | |
|
DPWG Guideline Annotation 1 |
Genotype
CYP2C19:*38/*38
|
|
|||
|
FDA Label Annotation 1 |
Genotype
CYP2C19:*38/*38
|
|
|||
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotype
CYP2C19:*38/*38
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 Genotypes and Dosing of Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2015. PMID:25974703
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for CYP2D6, CYP2C19, CYP2B6, SLC6A4, and HTR2A Genotypes and Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor Antidepressants. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2023. PMID:37032427
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
- Dutch Pharmacogenetics Working Group (DPWG) guideline for the gene-drug interaction between CYP2C19 and CYP2D6 and SSRIs. European journal of human genetics : EJHG. 2022. PMID:34782755
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product Celexa (citalopram), NDA020822, Allergan, Inc.
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
clomipramine
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Dosing Info
|
Genotype
Phenotypes
Activity Scores
|
|
Consider a 25% reduction of recommended starting dose. Utilize therapeutic drug monitoring to guide dose adjustments.
Other ConsiderationsPatients may receive an initial low dose of a tricyclic, which is then increased over several days to the recommended steady-state dose. The starting dose in this guideline refers to the recommended steady-state dose. Dosing recommendations only apply to higher initial doses of TCAs for treatment of conditions such as depression. See other considerations for dosing recommendations for conditions where lower initial doses are used, such as neuropathic pain. |
Optional |
|
Population: Dosing Info
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
The risk of side effects may be increased, because the gene variation leads to increased plasma concentrations of clomipramine and the active metabolite desmethylclomipramine. | Use 70% of the standard dose and monitor the effect and side effects or the plasma concentrations of clomipramine and desmethylclomipramine. For depression, the therapeutic range is 200-400 ng/mL for the sum of the plasma concentrations of clomipramine and desmethylclomipramine. For anxiety disorders, the therapeutic plasma concentration of clomipramine is approximately 100 ng/mL, in combination with a plasma concentration of desmethylclomipramine lower than 200 ng/mL. For obsessive compulsive disorder, the therapeutic plasma concentration of clomipramine is higher than 200 ng/mL, in combination with a plasma concentration of desmethylclomipramine that is as low as possible. A sum of the plasma concentrations of clomipramine and desmethylclomipramine higher than 600 ng/mL is considered toxic. | Unspecified |
|
Affected subgroup: CYP2D6 ultrarapid, intermediate, or poor metabolizers No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
"May alter systemic concentrations." * | Unspecified |
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guideline for CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 genotypes and dosing of tricyclic antidepressants. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2013. PMID:23486447
- Clinical pharmacogenetics implementation consortium guideline (CPIC) for CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 genotypes and dosing of tricyclic antidepressants: 2016 update. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2017. PMID:27997040
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
clopidogrel
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer |
CYP2C19: Normal clopidogrel active metabolite formation; normal on-treatment platelet reactivity |
If considering clopidogrel, use at standard dose (75 mg/day)
Other ConsiderationsFor cardiovascular indications of acute coronary syndrome (ACS) and/or percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). ACS and/or PCI includes patients undergoing PCI for an ACS or non-ACS (elective) indication. |
Strong | |
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer |
CYP2C19: Normal clopidogrel active metabolite formation; normal on-treatment platelet reactivity |
If considering clopidogrel, use at standard dose (75 mg/day)
Other ConsiderationsFor non-acute coronary syndrome (non-ACS) and non-percutaneous coronary intervention (non-PCI) cardiovascular indications. Non-ACS, non-PCI cardiovascular indications include peripheral arterial disease and stable coronary artery disease following a recent myocardial infarction outside the setting of PCI. |
Strong | |
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer |
CYP2C19: Normal clopidogrel active metabolite formation; normal on-treatment platelet reactivity |
If considering clopidogrel, use at standard dose (75 mg/day)
Other ConsiderationsFor neurovascular indications. Neurovascular disease includes acute ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack, secondary prevention of stroke, or prevention of thromboembolic events following neurointerventional procedures such as carotid artery stenting and stent-assisted coiling of intracranial aneurysms. |
Strong | |
|
DPWG Guideline Annotation 1 |
Genotype
CYP2C19:*38/*38
|
|
|||
|
FDA Label Annotation 1 |
Genotype
CYP2C19:*38/*38
|
|
|||
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotype
CYP2C19:*38/*38
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guidelines for cytochrome P450-2C19 (CYP2C19) genotype and clopidogrel therapy. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21716271
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guidelines for CYP2C19 genotype and clopidogrel therapy: 2013 update. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2013. PMID:23698643
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline for CYP2C19 Genotype and Clopidogrel Therapy: 2022 Update. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2022. PMID:35034351
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product Plavix (clopidogrel bisulfate), NDA020839, Rebel Distributors Corp.
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product Plavix (clopidogrel), sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC - NDA020839/SUPPL-78, 09/16/2022.
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
codeine
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Other Guidance
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
CYP2D6: Reduced morphine formation | Use codeine label recommended age- or weight-specific dosing. If no response and opioid use is warranted, consider a non-tramadol opioid. | Moderate | |
|
Population: Alternate Drug
Dosing Info
Other Guidance
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
The genetic variation reduces the conversion of codeine to morphine. This can result in reduced analgesia. |
For PAIN:
It is not possible to offer adequately substantiated advice for dose adjustment based on the limited available literature for this phenotype.
|
Unspecified | |
|
FDA Label Annotation 1 |
Genotype
CYP2D6:*1/*3
|
|
|||
|
Genotype
CYP2D6:*1/*3
|
|
||||
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) guidelines for codeine therapy in the context of cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6) genotype. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2012. PMID:22205192
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guidelines for cytochrome P450 2D6 genotype and codeine therapy: 2014 update. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2014. PMID:24458010
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline for CYP2D6, OPRM1, and COMT Genotypes and Select Opioid Therapy. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2021. PMID:33387367
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
- Dutch Pharmacogenetics Working Group (DPWG) guideline for the gene-drug interaction between CYP2D6 and opioids (codeine, tramadol and oxycodone). European journal of human genetics : EJHG. 2022. PMID:34267337
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product Codeine sulfate (codeine sulfate), NDA022402, West-Ward Pharmaceuticals Corp.
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
dapsone
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal |
G6PD: Low risk of acute hemolytic anemia | No reason to avoid based on G6PD status | Strong | |
|
FDA Label Annotation 1 |
Genotype
G6PD:B (reference)/B (reference)
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) guidelines for rasburicase therapy in the context of G6PD deficiency genotype. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2014. PMID:24787449
- Expanded Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline for Medication Use in the Context of G6PD Genotype. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2023. PMID:36049896
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product DAPSONE (dapsone), Pacific Pharma, Inc. - NDA021794/SUPPL-16, 05/18/2018.
desflurane
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Other Guidance
|
Genotype
Phenotypes
|
These results do not eliminate the chance that this patient is susceptible to malignant hyperthermia (MH). The genetic cause of about half of all MH survivors, with MH susceptibility confirmed by contracture test, remains unknown (PMID 28902675). | Clinical findings, family history, further genetic testing and other laboratory data should guide use of halogenated volatile anesthetics or depolarizing muscle relaxants. | Strong |
|
Population: Alternate Drug
|
Genotype
Phenotypes
|
"The use of SUPRANE [desflurane] is contraindicated in...[cases of k]nown or suspected genetic susceptibility to malignant hyperthermia...SUPRANE [desflurane] can induce malignant hyperthermia in patients with known or suspected susceptibility based on genetic factors or family history, including those with certain inherited ryanodine receptor (RYR1) or dihydropyridine receptor (CACNA1S) variants. " See label for more information. * | Unspecified |
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for the Use of Potent Volatile Anesthetic Agents and Succinylcholine in the Context of RYR1 or CACNA1S Genotypes. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2019. PMID:30499100
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product SUPRANE (desflurane), NDA020118, Baxter Healthcare Corporation.
desipramine
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Dosing Info
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
CYP2D6: Reduced metabolism of TCAs to less active compounds compared to normal metabolizers. Higher plasma concentrations of active drug will increase the probability of side effects. |
Consider a 25% reduction of recommended starting dose. Titrate dose to observed clinical response with symptom improvement and minimal (if any) side effects. Utilize therapeutic drug monitoring to guide dose adjustments.
Other ConsiderationsPatients may receive an initial low dose of a tricyclic, which is then increased over several days to the recommended steady-state dose. The starting dose in this guideline refers to the recommended steady-state dose. Dosing recommendations only apply to higher initial doses of TCAs for treatment of conditions such as depression. See other considerations for dosing recommendations for conditions where lower initial doses are used, such as neuropathic pain. |
Optional |
|
Affected subgroup: CYP2D6 ultrarapid, intermediate, or poor metabolizers No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
"May alter systemic concentrations." * | Unspecified |
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guideline for CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 genotypes and dosing of tricyclic antidepressants. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2013. PMID:23486447
- Clinical pharmacogenetics implementation consortium guideline (CPIC) for CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 genotypes and dosing of tricyclic antidepressants: 2016 update. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2017. PMID:27997040
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
dexlansoprazole
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Dosing Info
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer |
CYP2C19: Normal PPI metabolism; may be at increased risk of therapeutic failure compared to CYP2C19 IMs and PMs | Initiate standard starting daily dose. Consider increasing dose by 50-100% for the treatment of H. pylori infection and erosive esophagitis. Daily dose may be given in divided doses. Monitor for efficacy. | Optional | |
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotype
CYP2C19:*38/*38
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for CYP2C19 and Proton Pump Inhibitor Dosing. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2021. PMID:32770672
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
doxepin
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Dosing Info
|
Genotype
Phenotypes
Activity Scores
|
|
Consider a 25% reduction of recommended starting dose. Utilize therapeutic drug monitoring to guide dose adjustments.
Other ConsiderationsPatients may receive an initial low dose of a tricyclic, which is then increased over several days to the recommended steady-state dose. The starting dose in this guideline refers to the recommended steady-state dose. Dosing recommendations only apply to higher initial doses of TCAs for treatment of conditions such as depression. See other considerations for dosing recommendations for conditions where lower initial doses are used, such as neuropathic pain. |
Optional |
|
Population: Dosing Info
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
The risk of side effects may be increased, because the gene variation leads to increased plasma concentrations of doxepin and the active metabolite nordoxepin. | Use 80% of the standard dose and monitor the effect and side effects or the plasma concentrations of doxepin and nordoxepin in order to set the maintenance dose. The therapeutic range is 100-250 ng/mL for the sum of doxepin and nordoxepin plasma concentrations. Values higher than 400 ng/mL are considered toxic. | Unspecified |
|
Affected subgroup: CYP2D6 ultrarapid, intermediate, or poor metabolizers No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
"May alter systemic concentrations." * | Unspecified |
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guideline for CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 genotypes and dosing of tricyclic antidepressants. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2013. PMID:23486447
- Clinical pharmacogenetics implementation consortium guideline (CPIC) for CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 genotypes and dosing of tricyclic antidepressants: 2016 update. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2017. PMID:27997040
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
efavirenz
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer |
CYP2B6: Normal efavirenz metabolism |
Initiate efavirenz with standard dosing (600 mg/day)
Other ConsiderationsThe ENCORE study showed that in treatment-naïve patients randomized to initiate efavirenz-based regimens (combined with tenofovir and emtricitabine), 400 mg/day was non-inferior to 600 mg/day regardless of CYP2B6 genotype (PMID 24522178). |
Strong | |
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer |
The guideline does not provide a description of the impact of a normal metabolizer phenotype on efavirenz. | The guideline does not provide a recommendation for efavirenz in normal metabolizers. | No recommendation | |
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotype
CYP2B6:*1/*1
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for CYP2B6 and Efavirenz-Containing Antiretroviral Therapy. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2019. PMID:31006110
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
eliglustat
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Alternate Drug
Dosing Info
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
This gene variation reduces the conversion of eliglustat to inactive metabolites. However, in the absence of CYP2D6 and CYP3A inhibitors, this does not result in a clinically significant increased risk of side effects. |
Co-medication with BOTH a MODERATE to STRONG CYP2D6 INHIBITOR AND a MODERATE to STRONG CYP3A INHIBITOR:
|
Unspecified |
|
Population: Dosing Info
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
CYP2D6 IMs have a recommended dose of 84 mg orally twice daily. * | Unspecified | |
|
Affected subgroup: CYP2D6 ultrarapid, normal, intermediate, or poor metabolizers Other Guidance
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
"Alters systemic concentrations, effectiveness, and adverse reaction risk (QT prolongation). Indicated for normal, intermediate, and poor metabolizer patients. Ultrarapid metabolizers may not achieve adequate concentrations to achieve a therapeutic effect. The recommended dosages are based on CYP2D6 metabolizer status. Coadministration with strong CYP3A inhibitors is contraindicated in intermediate and poor CYP2D6 metabolizers. Refer to FDA labeling for specific dosing recommendations." * | Unspecified |
enflurane
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Other Guidance
|
Genotype
Phenotypes
|
These results do not eliminate the chance that this patient is susceptible to malignant hyperthermia (MH). The genetic cause of about half of all MH survivors, with MH susceptibility confirmed by contracture test, remains unknown (PMID 28902675). | Clinical findings, family history, further genetic testing and other laboratory data should guide use of halogenated volatile anesthetics or depolarizing muscle relaxants. | Strong |
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for the Use of Potent Volatile Anesthetic Agents and Succinylcholine in the Context of RYR1 or CACNA1S Genotypes. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2019. PMID:30499100
escitalopram
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer |
CYP2C19: Normal metabolism | Initiate therapy with recommended starting dose | Strong | |
|
DPWG Guideline Annotation 1 |
Genotype
CYP2C19:*38/*38
|
|
|||
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotype
CYP2C19:*38/*38
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 Genotypes and Dosing of Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2015. PMID:25974703
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for CYP2D6, CYP2C19, CYP2B6, SLC6A4, and HTR2A Genotypes and Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor Antidepressants. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2023. PMID:37032427
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
- Dutch Pharmacogenetics Working Group (DPWG) guideline for the gene-drug interaction between CYP2C19 and CYP2D6 and SSRIs. European journal of human genetics : EJHG. 2022. PMID:34782755
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
flecainide
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Dosing Info
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
The genetic variation reduces conversion of flecainide to inactive metabolites. This may increase the risk of side effects. |
Indications other than diagnosis of Brugada syndrome:
|
Unspecified |
Citations:
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
flucloxacillin
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Alternate Drug
Other Guidance
|
Genotype
Phenotype
*57:01 positive |
HLA-B*57:01-positive patients have an 80-fold elevated risk of flucloxacillin-induced liver injury. However, the incidence is low (1-2 per 1000 individuals). |
|
Unspecified |
flucytosine
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
2.0 (Normal Metabolizer) |
The guideline does not provide a description of the impact of a DPYD activity score of 2 on flucytosine. | The guideline does not provide a recommendation for flucytosine in patients with a DPYD activity score of 2. | No recommendation |
fluorouracil
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer Activity Score
2.0 |
DPYD: Normal DPD activity and "normal" risk for fluoropyrimidine toxicity | Based on genotype, there is no indication to change dose or therapy. Use label-recommended dosage and administration. | Strong | |
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
2.0 (Normal Metabolizer) |
The guideline does not provide a description of the impact of a DPYD activity score of 2 on fluorouracil. | The guideline does not provide a recommendation for fluorouracil in patients with a DPYD activity score of 2. | No recommendation | |
|
FDA Label Annotation 1 |
Genotype
DPYD:Reference/Reference
|
|
|||
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotype
DPYD:Reference/Reference
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guidelines for dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase genotype and fluoropyrimidine dosing. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2013. PMID:23988873
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for Dihydropyrimidine Dehydrogenase Genotype and Fluoropyrimidine Dosing: 2017 Update. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2018. PMID:29152729
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
- Dutch Pharmacogenetics Working Group (DPWG) guideline for the gene-drug interaction of DPYD and fluoropyrimidines. European journal of human genetics : EJHG. 2020. PMID:31745289
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product Carac (fluorouracil), Bausch Health US, LLC - NDA020985/SUPPL-19, 05/26/2022.
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product FLUOROURACIL (FLUOROURACIL), Eugia US LLC - ANDA202669/SUPPL-9, 03/21/2024.
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product Fluorouracil (Fluorouracil), BluePoint Laboratories - ANDA210124/SUPPL-9, 03/21/2024.
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
flurbiprofen
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer Activity Score
2.0 |
CYP2C9: Normal metabolism | Initiate therapy with recommended starting dose. In accordance with the prescribing information, use the lowest effective dosage for shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals. | Strong | |
|
FDA Label Annotation 1 |
Genotype
CYP2C9:*1/*1
|
|
|||
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotype
CYP2C9:*1/*1
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline (CPIC) for CYP2C9 and Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2020. PMID:32189324
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product FLURBIPROFEN SODIUM (flurbiprofen sodium), NDA019404, Rebel Distributors Corp.
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product flurbiprofen (NDA018766)
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
fluvastatin
In case no genotype can be determined, recommendations are based on the rs4149056 genotype alone as per guideline. The minor C allele at rs4149056 defines SLCO1B1*5.
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotypes
Activity Scores
|
|
Prescribe desired starting dose and adjust doses of fluvastatin based on disease-specific guidelines.
Other ConsiderationsThe potential for drug-drug interactions and dose limits based on renal and hepatic function and ancestry should be evaluated prior to initiating a statin. |
Strong |
Citations:
- The Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline for SLCO1B1, ABCG2, and CYP2C9 genotypes and Statin-Associated Musculoskeletal Symptoms. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2022. PMID:35152405
fluvoxamine
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
CYP2D6: Reduced metabolism of fluvoxamine to less active compounds when compared to CYP2D6 normal metabolizers. Higher plasma concentrations may increase the probability of side effects. | Initiate therapy with recommended starting dose. | Moderate | |
|
Population: Other Guidance
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
The fluvoxamine label states: "Caution is indicated in patients known to have reduced levels of cytochrome P450 2D6 activity[...]" See label for more information. * | Unspecified | ||
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotype
CYP2D6:*1/*3
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 Genotypes and Dosing of Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2015. PMID:25974703
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for CYP2D6, CYP2C19, CYP2B6, SLC6A4, and HTR2A Genotypes and Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor Antidepressants. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2023. PMID:37032427
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product fluvoxamine maleate (Fluvoxamine maleate), NDA021519, Bryant Ranch Prepack.
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
fosphenytoin
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Alternate Drug
|
Genotype
Phenotypes
Activity Scores
|
|
If patient is phenytoin-naive, do not use phenytoin/fosphenytoin. Avoid carbamazepine and oxcarbazepine.
Other ConsiderationsOther aromatic anticonvulsants, including eslicarbazepine, lamotrigine, and phenobarbital, have weaker evidence linking SJS/TEN with the HLA-B*15:02 allele; however, caution should still be used in choosing an alternative agent. |
Strong |
|
Population: Other Guidance
|
Genotype
Phenotypes
Activity Scores
|
|
If the patient has previously used phenytoin continuously for longer than three months without incidence of cutaneous adverse reactions, cautiously consider use of phenytoin in the future. The latency period for drug-induced SJS/TEN is short with continuous dosing and adherence to therapy (4-28 days), and cases usually occur within three months of dosing.
Other ConsiderationsPrevious tolerance of phenytoin is not indicative of tolerance to other aromatic anticonvulsants. |
Optional |
|
Population: Alternate Drug
|
Genotype
Phenotypes
Activity Scores
|
"Consider avoiding CEREBYX [fosphenytoin] as an alternative to carbamazepine in patients who are positive for HLA-B*1502 or in CYP2C9*3 carriers." See label for more information. * | Unspecified | |
|
HLA-B*15:02 allele positive Alternate Drug
|
Genotype
Phenotype
*15:02 positive |
"May result in higher adverse reaction risk (severe cutaneous reactions). Patients positive for HLA-B*15:02 may be at increased risk of Stevens Johnson Syndrome/Toxic Epidermal necrolysis (SJS/TEN). Consider avoiding fosphenytoin as an alternative to carbamazepine in patients who are positive for HLA-B*15:02. Genotyping is not a substitute for clinical vigilance and patient management." * | Unspecified |
Citations:
- Clinical pharmacogenetics implementation consortium guidelines for CYP2C9 and HLA-B genotypes and phenytoin dosing. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2014. PMID:25099164
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for CYP2C9 and HLA-B Genotypes and Phenytoin Dosing: 2020 Update. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2021. PMID:32779747
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product CEREBYX (Fosphenytoin Sodium), NDA020450, Pfizer Laboratories Div Pfizer Inc.
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
haloperidol
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
The genetic variation results in a higher plasma concentration, but the effect is small and no clinically significant effects were found. | NO action is required for this gene-drug interaction. | Unspecified |
Citations:
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
- Dutch Pharmacogenetics Working Group (DPWG) guideline for the gene-drug interaction between CYP2D6, CYP3A4 and CYP1A2 and antipsychotics. European journal of human genetics : EJHG. 2024. PMID:37002327
halothane
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Other Guidance
|
Genotype
Phenotypes
|
These results do not eliminate the chance that this patient is susceptible to malignant hyperthermia (MH). The genetic cause of about half of all MH survivors, with MH susceptibility confirmed by contracture test, remains unknown (PMID 28902675). | Clinical findings, family history, further genetic testing and other laboratory data should guide use of halogenated volatile anesthetics or depolarizing muscle relaxants. | Strong |
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for the Use of Potent Volatile Anesthetic Agents and Succinylcholine in the Context of RYR1 or CACNA1S Genotypes. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2019. PMID:30499100
hydrocodone
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Other Guidance
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
CYP2D6: Minimal evidence for pharmacokinetic or clinical effect. | Use hydrocodone label recommended age- or weight-specific dosing. If no response and opioid use is warranted, consider non-codeine or non-tramadol opioid. | Optional |
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline for CYP2D6, OPRM1, and COMT Genotypes and Select Opioid Therapy. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2021. PMID:33387367
ibuprofen
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer Activity Score
2.0 |
CYP2C9: Normal metabolism | Initiate therapy with recommended starting dose. In accordance with the prescribing information, use the lowest effective dosage for shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals. | Strong | |
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotype
CYP2C9:*1/*1
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline (CPIC) for CYP2C9 and Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2020. PMID:32189324
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
imipramine
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Dosing Info
|
Genotype
Phenotypes
Activity Scores
|
|
Consider a 25% reduction of recommended starting dose. Utilize therapeutic drug monitoring to guide dose adjustments.
Other ConsiderationsPatients may receive an initial low dose of a tricyclic, which is then increased over several days to the recommended steady-state dose. The starting dose in this guideline refers to the recommended steady-state dose. Dosing recommendations only apply to higher initial doses of TCAs for treatment of conditions such as depression. See other considerations for dosing recommendations for conditions where lower initial doses are used, such as neuropathic pain. |
Optional |
|
Population: Dosing Info
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
The risk of side effects may be increased, because the gene variation leads to increased plasma concentrations of imipramine and desipramine. | Use 70% of the standard dose and monitor the effect and side effects or the plasma concentrations of imipramine and desipramine in order to set the maintenance dose. The therapeutic range is 150-300 ng/mL for the sum of the imipramine and desipramine plasma concentrations. Values exceeding 500 ng/mL are considered toxic. | Unspecified |
|
Affected subgroup: CYP2D6 ultrarapid, intermediate, or poor metabolizers No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
"May alter systemic concentrations." * | Unspecified |
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guideline for CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 genotypes and dosing of tricyclic antidepressants. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2013. PMID:23486447
- Clinical pharmacogenetics implementation consortium guideline (CPIC) for CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 genotypes and dosing of tricyclic antidepressants: 2016 update. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2017. PMID:27997040
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
irinotecan
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer |
The guideline does not provide a description of the impact of a normal metabolizer phenotype on irinotecan. | The guideline does not provide a recommendation for irinotecan in normal metabolizers | No recommendation | |
|
FDA Label Annotation 1 |
Genotype
UGT1A1:*1/*1
|
|
|||
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotype
UGT1A1:*1/*1
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
- Dutch pharmacogenetics working group (DPWG) guideline for the gene-drug interaction between UGT1A1 and irinotecan. European journal of human genetics : EJHG. 2023. PMID:36443464
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product Camptosar (irinotecan hydrochloride), Pharmacia & Upjohn Company LLC - NDA020571/SUPPL-53, 01/27/2022.
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product Onivyde (IRINOTECAN HYDROCHLORIDE), Ipsen Biopharmaceuticals, Inc. - NDA207793/SUPPL-16, 02/13/2024.
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
isoflurane
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Other Guidance
|
Genotype
Phenotypes
|
These results do not eliminate the chance that this patient is susceptible to malignant hyperthermia (MH). The genetic cause of about half of all MH survivors, with MH susceptibility confirmed by contracture test, remains unknown (PMID 28902675). | Clinical findings, family history, further genetic testing and other laboratory data should guide use of halogenated volatile anesthetics or depolarizing muscle relaxants. | Strong |
|
Population: Alternate Drug
|
Genotype
Phenotypes
|
"CONTRAINDICATIONS...with known or suspected genetic susceptibility to malignant hyperthermia...FORANE [isoflurane] can induce malignant hyperthermia in patients with known or suspected susceptibility based on genetic factors or family history, including those with certain inherited ryanodine receptor (RYR1) or dihydropyridine receptor (CACNA1S) variants." See label for more information. * | Unspecified |
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for the Use of Potent Volatile Anesthetic Agents and Succinylcholine in the Context of RYR1 or CACNA1S Genotypes. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2019. PMID:30499100
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product FORANE (isoflurane), NDA017624, Baxter Healthcare Corporation.
ivacaftor
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Alternate Drug
|
Genotype
Phenotype
ivacaftor non-responsive in CF patients |
CFTR: An individual diagnosed with cystic fibrosis (CF) and negative for a CFTR variant listed in the FDA-approved drug label as being responsive to ivacaftor. | Ivacaftor is not recommended | Moderate | |
|
FDA Label Annotation 1 |
Genotype
CFTR:Reference/Reference
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) guidelines for ivacaftor therapy in the context of CFTR genotype. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2014. PMID:24598717
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product Kalydeco (ivacaftor), NDA203188, Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated.
lamotrigine
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Alternate Drug
Other Guidance
|
Genotype
Phenotype
*15:02 positive |
The life-threatening cutaneous side effect Stevens-Johnson Syndrome/Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (SJS/TEN) in the first three months occurs more often in patients with this genetic variation. Based on the estimated risk for all patients and the increase by a factor 2.4-7.9 for patients with this genetic variation, the risk of lamotrigine-induced SJS/TEN in patients with HLA-B*1502 is estimated at 0.24-0.79%. |
|
Unspecified |
Citations:
- Dutch Pharmacogenetics Working Group (DPWG) guideline for the gene-drug interaction of CYP2C9, HLA-A and HLA-B with anti-epileptic drugs. European journal of human genetics : EJHG. 2024. PMID:38570725
lansoprazole
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Dosing Info
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer |
CYP2C19: Normal PPI metabolism; may be at increased risk of therapeutic failure compared to CYP2C19 IMs and PMs | Initiate standard starting daily dose. Consider increasing dose by 50-100% for the treatment of H. pylori infection and erosive esophagitis. Daily dose may be given in divided doses. Monitor for efficacy. | Moderate | |
|
DPWG Guideline Annotation 1 |
Genotype
CYP2C19:*38/*38
|
|
|||
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotype
CYP2C19:*38/*38
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for CYP2C19 and Proton Pump Inhibitor Dosing. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2021. PMID:32770672
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
lornoxicam
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer Activity Score
2.0 |
CYP2C9: Normal metabolism | Initiate therapy with recommended starting dose. In accordance with the prescribing information, use the lowest effective dosage for shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals. | Strong |
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline (CPIC) for CYP2C9 and Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2020. PMID:32189324
lovastatin
In case no genotype can be determined, recommendations are based on the rs4149056 genotype alone as per guideline. The minor C allele at rs4149056 defines SLCO1B1*5.
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Function |
SLCO1B1: Typical myopathy risk and statin exposure |
Prescribe desired starting dose and adjust doses based on disease-specific guidelines.
Other ConsiderationsThe potential for drug-drug interactions and dose limits based on renal and hepatic function and ancestry should be evaluated prior to initiating a statin. |
Strong |
Citations:
- The Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline for SLCO1B1, ABCG2, and CYP2C9 genotypes and Statin-Associated Musculoskeletal Symptoms. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2022. PMID:35152405
meclizine
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Other Guidance
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
"The genetic polymorphism of CYP2D6 that results in poor-, intermediate-, extensive-, and ultrarapid metabolizer phenotypes could contribute to large inter-individual variability in meclizine exposure." | "... when ANTIVERT® [meclizine] is administered to patients with CYP2D6 polymorphism, monitor for adverse reactions and clinical effect accordingly." See label for more information. * | Unspecified |
|
Affected subgroup: CYP2D6 ultrarapid, intermediate, or poor metabolizers Other Guidance
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
"May affect systemic concentrations. Monitor for adverse reactions and clinical effect." * | Unspecified |
meloxicam
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer Activity Score
2.0 |
CYP2C9: Normal metabolism | Initiate therapy with recommended starting dose. In accordance with the prescribing information, use the lowest effective dosage for shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals. | Strong | |
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotype
CYP2C9:*1/*1
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline (CPIC) for CYP2C9 and Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2020. PMID:32189324
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
mercaptopurine
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotypes
|
|
Start with normal starting dose (e.g., 75 mg/m2/day or 1.5 mg/kg/day) and adjust doses of mercaptopurine (and of any other myelosuppressive therapy) without any special emphasis on mercaptopurine compared to other agents. Allow at least 2 weeks to reach steady-state after each dose adjustment (PMID 20354201, 16401827, 11302950).
Other ConsiderationsNormal starting doses vary by race/ethnicity and treatment regimens. If standard dose is below normal recommended dose, dose reduction might not be recommended for intermediate metabolizers. |
Strong | |
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer |
The guideline does not provide a description of the impact of a normal metabolizer phenotype on mercaptopurine. | The guideline does not provide a recommendation for mercaptopurine in normal metabolizers | No recommendation | |
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer |
The guideline does not provide a description of the impact of a normal metabolizer phenotype on mercaptopurine. | The guideline does not provide a recommendation for mercaptopurine in normal metabolizers. | No recommendation | |
|
FDA Label Annotation 1 |
Genotypes
NUDT15:*1/*1;TPMT:*1/*1 |
|
|||
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotypes
NUDT15:*1/*1;TPMT:*1/*1 |
|
|||
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guidelines for thiopurine methyltransferase genotype and thiopurine dosing. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21270794
- Clinical pharmacogenetics implementation consortium guidelines for thiopurine methyltransferase genotype and thiopurine dosing: 2013 update. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2013. PMID:23422873
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline for Thiopurine Dosing Based on TPMT and NUDT15 Genotypes: 2018 Update. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2019. PMID:30447069
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product PURINETHOL (Mercaptopurine), Quinn Pharmaceuticals - NDA009053/SUPPL-40, 12/29/2020.
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product PURIXAN (mercaptopurine), Nova Laboratories, Ltd - NDA205919/SUPPL-4, 04/07/2020.
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
methoxyflurane
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Other Guidance
|
Genotype
Phenotypes
|
These results do not eliminate the chance that this patient is susceptible to malignant hyperthermia (MH). The genetic cause of about half of all MH survivors, with MH susceptibility confirmed by contracture test, remains unknown (PMID 28902675). | Clinical findings, family history, further genetic testing and other laboratory data should guide use of halogenated volatile anesthetics or depolarizing muscle relaxants. | Strong |
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for the Use of Potent Volatile Anesthetic Agents and Succinylcholine in the Context of RYR1 or CACNA1S Genotypes. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2019. PMID:30499100
methylene blue
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal |
G6PD: Low risk of acute hemolytic anemia | No reason to avoid based on G6PD status | Strong | |
|
FDA Label Annotation 1 |
Genotype
G6PD:B (reference)/B (reference)
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) guidelines for rasburicase therapy in the context of G6PD deficiency genotype. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2014. PMID:24787449
- Expanded Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline for Medication Use in the Context of G6PD Genotype. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2023. PMID:36049896
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product PROVAYBLUE (methylene blue), NDA204630, American Regent, Inc.
metoprolol
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
Decreased metabolism of metoprolol leading to increased drug concentrations; however, this does not appear to translate into clinically significant changes in heart rate, blood pressure, or clinical outcomes | Initiate standard dosing | Moderate | |
|
Population: Dosing Info
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
The gene variation reduces the conversion of metoprolol to inactive metabolites. However, the clinical consequences are limited mainly to the occurrence of asymptomatic bradycardia. |
If a GRADUAL REDUCTION in HEART RATE is desired, or in the event of SYMPTOMATIC BRADYCARDIA:
|
Unspecified | |
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotype
CYP2D6:*1/*3
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline (CPIC) for CYP2D6, ADRB1, ADRB2, ADRA2C, GRK4, and GRK5 Genotypes and Beta-Blocker Therapy. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2024. PMID:38951961
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
nitrofurantoin
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal |
G6PD: Low risk of acute hemolytic anemia | No reason to avoid based on G6PD status | Strong | |
|
FDA Label Annotation 1 |
Genotype
G6PD:B (reference)/B (reference)
|
|
|||
nortriptyline
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Dosing Info
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
CYP2D6: Reduced metabolism of tricyclic antidepressants to less active compounds compared to normal metabolizers. Higher plasma concentrations of active drug will increase the probability of side effects. |
Consider a 25% reduction of recommended starting dose. Titrate dose to observed clinical response with symptom improvement and minimal (if any) side effects. Utilize therapeutic drug monitoring to guide dose adjustments.
Other ConsiderationsPatients may receive an initial low dose of a tricyclic, which is then increased over several days to the recommended steady-state dose. The starting dose in this guideline refers to the recommended steady-state dose. Dosing recommendations only apply to higher initial doses of tricyclic antidepressants for treatment of conditions such as depression. See other considerations for dosing recommendations for conditions where lower initial doses are used, such as neuropathic pain. |
Optional |
|
Population: Dosing Info
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
The risk of side effects may be increased, because the gene variation leads to an increased plasma concentration of nortriptyline. | Use 60% of the standard dose and monitor the effect and side effects or the plasma concentration of nortriptyline in order to set the maintenance dose. The therapeutic range of nortriptyline is 50-150 ng/mL. Values exceeding 250 ng/mL are considered toxic. | Unspecified |
|
Affected subgroup: CYP2D6 ultrarapid, intermediate, or poor metabolizers No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
"May alter systemic concentrations." * | Unspecified |
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guideline for CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 genotypes and dosing of tricyclic antidepressants. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2013. PMID:23486447
- Clinical pharmacogenetics implementation consortium guideline (CPIC) for CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 genotypes and dosing of tricyclic antidepressants: 2016 update. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2017. PMID:27997040
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
omeprazole
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Dosing Info
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer |
CYP2C19: Normal PPI metabolism; may be at increased risk of therapeutic failure compared to CYP2C19 IMs and PMs | Initiate standard starting daily dose. Consider increasing dose by 50-100% for the treatment of H. pylori infection and erosive esophagitis. Daily dose may be given in divided doses. Monitor for efficacy. | Moderate | |
|
DPWG Guideline Annotation 1 |
Genotype
CYP2C19:*38/*38
|
|
|||
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotype
CYP2C19:*38/*38
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for CYP2C19 and Proton Pump Inhibitor Dosing. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2021. PMID:32770672
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
ondansetron
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
CYP2D6: Very limited data available for CYP2D6 intermediate metabolizers |
Insufficient evidence demonstrating clinical impact based on CYP2D6 genotype. Initiate therapy with recommended starting dose.
Other ConsiderationsDrug-drug interactions and other patient characteristics (e.g., age, renal function, and liver function) should be considered when selecting alternative therapy. |
No recommendation |
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) guideline for CYP2D6 genotype and use of ondansetron and tropisetron. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2017. PMID:28002639
oxcarbazepine
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Alternate Drug
|
Genotype
Phenotype
*15:02 positive |
HLA-B: Greater risk of oxcarbazepine-induced SJS/TEN |
If patient is oxcarbazepine-naïve, do not use oxcarbazepine.
Other ConsiderationsOther aromatic anticonvulsants have weaker evidence linking SJS/TEN with the HLA-B*15:02 allele; however, caution should still be used in choosing an alternative agent. Aromatic anticonvulsants include carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, eslicarbazepine, lamotrigine, phenytoin, fosphenytoin, and phenobarbital. |
Strong |
|
Population: Other Guidance
|
Genotype
Phenotype
*15:02 positive |
HLA-B: Greater risk of oxcarbazepine-induced SJS/TEN |
The latency period for drug-induced SJS/TEN is short with continuous dosing and adherence to therapy (~4-28 days), and cases usually occur within three months of dosing; therefore, if the patient has previously used oxcarbazepine consistently for longer than three months without incidence of cutaneous adverse reactions, cautiously consider use of oxcarbazepine in the future.
Other ConsiderationsPrevious tolerance of oxcarbazepine is not indicative of tolerance to other aromatic anticonvulsants. Aromatic anticonvulsants include carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, eslicarbazepine, lamotrigine, phenytoin, fosphenytoin, and phenobarbital. |
Optional |
|
Population: Alternate Drug
Other Guidance
|
Genotype
Phenotype
*15:02 positive |
Stevens-Johnson syndrome, the severe cutaneous side effect in the first three months that can potentially result in permanent damage, occurs more often in patients with this genetic variation. The calculated risk of oxcarbazepine-induced SJS in patients with HLA-B*1502 is 0.73%. |
|
Unspecified |
|
Population: Alternate Drug
|
Genotype
Phenotype
*15:02 positive |
"The use of oxcarbazepine should be avoided in patients positive for HLA-B*1502 unless the benefits clearly outweigh the risks." See label for more information. * | Unspecified | |
|
Affected subgroup: HLA-B*15:02 allele positive Other Guidance
|
Genotype
Phenotype
*15:02 positive |
"Results in higher adverse reaction risk (severe skin reactions). Patients positive for HLA-B*15:02 may be at increased risk of severe skin reactions with other drugs that are associated with a risk of Stevens Johnson Syndrome/Toxic Epidermal necrolysis (SJS/TEN). Genotyping is not a substitute for clinical vigilance." * | Unspecified |
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline for HLA Genotype and Use of Carbamazepine and Oxcarbazepine: 2017 Update. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2018. PMID:29392710
- Dutch Pharmacogenetics Working Group (DPWG) guideline for the gene-drug interaction of CYP2C9, HLA-A and HLA-B with anti-epileptic drugs. European journal of human genetics : EJHG. 2024. PMID:38570725
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product OXTELLAR XR (OXCARBAZEPINE), NDA202810, Supernus Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
pantoprazole
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Dosing Info
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer |
CYP2C19: Normal PPI metabolism; may be at increased risk of therapeutic failure compared to CYP2C19 IMs and PMs | Initiate standard starting daily dose. Consider increasing dose by 50-100% for the treatment of H. pylori infection and erosive esophagitis. Daily dose may be given in divided doses. Monitor for efficacy. | Moderate | |
|
DPWG Guideline Annotation 1 |
Genotype
CYP2C19:*38/*38
|
|
|||
|
FDA Label Annotation 1 |
Genotype
CYP2C19:*38/*38
|
|
|||
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotype
CYP2C19:*38/*38
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for CYP2C19 and Proton Pump Inhibitor Dosing. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2021. PMID:32770672
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product Protonix Delayed-Release (PANTOPRAZOLE SODIUM), NDA020987, Avera McKennan Hospital.
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
paroxetine
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Dosing Info
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
CYP2D6: Reduced metabolism of paroxetine to less active compounds when compared to CYP2D6 normal metabolizers when starting treatment or at lower doses. Higher plasma concentrations may increase the probability of side effects. Paroxetine-associated phenoconversion of intermediate metabolizers to poor metabolizers due to CYP2D6 autoinhibition may occur and is dose-dependent and greater at steady state concentrations. |
Consider a lower starting dose and slower titration schedule as compared to normal metabolizers.
Other ConsiderationsDrug-drug interactions and other patient characteristics (e.g., age, renal function, liver function) should be considered when adjusting dose or selecting an alternative therapy. |
Optional |
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
The plasma concentration of paroxetine can increase as a result of the reduced activity of CYP2D6. However, studies did not find any clinical effects. | NO action is needed for this gene-drug interaction. | Unspecified |
|
Affected subgroup: CYP2D6 ultrarapid, intermediate, or poor metabolizers No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
"May alter systemic concentrations." * | Unspecified |
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 Genotypes and Dosing of Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2015. PMID:25974703
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for CYP2D6, CYP2C19, CYP2B6, SLC6A4, and HTR2A Genotypes and Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor Antidepressants. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2023. PMID:37032427
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
- Dutch Pharmacogenetics Working Group (DPWG) guideline for the gene-drug interaction between CYP2C19 and CYP2D6 and SSRIs. European journal of human genetics : EJHG. 2022. PMID:34782755
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
pazopanib
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Affected subgroup: HLA-B*57:01 allele positive Other Guidance
|
Genotype
Phenotype
*57:01 positive |
"May result in higher adverse reaction risk (liver enzyme elevations). Monitor liver function tests regardless of genotype." * | Unspecified |
Citations:
pegloticase
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal |
G6PD: Low risk of acute hemolytic anemia | No reason to avoid based on G6PD status | Strong | |
|
FDA Label Annotation 1 |
Genotype
G6PD:B (reference)/B (reference)
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) guidelines for rasburicase therapy in the context of G6PD deficiency genotype. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2014. PMID:24787449
- Expanded Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline for Medication Use in the Context of G6PD Genotype. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2023. PMID:36049896
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product Krystexxa (pegloticase), BLA125293, Horizon Pharma Inc.
phenprocoumon
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
-1639 GG |
The guideline does not provide a description of the impact of the VKORC1 rs9923231 CC genotype (-1639 GG genotype) on phenprocoumon. | The guideline does not provide a recommendation for phenprocoumon in patients with the VKORC1 rs9923231 CC genotype (-1639 GG genotype). | No recommendation |
Citations:
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
phenytoin
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Alternate Drug
|
Genotype
Phenotypes
Activity Scores
|
|
If patient is phenytoin-naive, do not use phenytoin/fosphenytoin. Avoid carbamazepine and oxcarbazepine.
Other ConsiderationsOther aromatic anticonvulsants, including eslicarbazepine, lamotrigine, and phenobarbital, have weaker evidence linking SJS/TEN with the HLA-B*15:02 allele; however, caution should still be used in choosing an alternative agent. |
Strong |
|
Population: Other Guidance
|
Genotype
Phenotypes
Activity Scores
|
|
If the patient has previously used phenytoin continuously for longer than three months without incidence of cutaneous adverse reactions, cautiously consider use of phenytoin in the future. The latency period for drug-induced SJS/TEN is short with continuous dosing and adherence to therapy (4-28 days), and cases usually occur within three months of dosing.
Other ConsiderationsPrevious tolerance of phenytoin is not indicative of tolerance to other aromatic anticonvulsants. |
Optional |
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer |
The guideline does not provide a description of the impact of a normal metabolizer phenotype on phenytoin. | The guideline does not provide a recommendation for phenytoin in normal metabolizers. | No recommendation |
|
Population: Alternate Drug
Other Guidance
|
Genotype
Phenotype
*15:02 positive |
The life-threatening cutaneous side effect Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis (SJS/TEN) in the first three months occurs more frequently in patients with this genetic variation. The calculated risk of phenytoin-induced SJS/TEN in patients with HLA-B*1502 is 0.65%. |
|
Unspecified |
|
Population: Alternate Drug
|
Genotype
Phenotypes
Activity Scores
|
"Consider avoiding DILANTIN [phenytoin] as an alternative to carbamazepine in patients who are positive for HLA-B*1502 or in CYP2C9*3 carriers." See label for more information. * | Unspecified | |
|
HLA-B*15:02 allele positive Alternate Drug
|
Genotype
Phenotype
*15:02 positive |
"May result in higher adverse reaction risk (severe cutaneous reactions). Patients positive for HLA-B*15:02 may be at increased risk of Stevens Johnson Syndrome/Toxic Epidermal necrolysis (SJS/TEN). Consider avoiding phenytoin as an alternative to carbamazepine in patients who are positive for HLA-B*15:02. Genotyping is not a substitute for clinical vigilance and patient management." * | Unspecified |
Citations:
- Clinical pharmacogenetics implementation consortium guidelines for CYP2C9 and HLA-B genotypes and phenytoin dosing. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2014. PMID:25099164
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for CYP2C9 and HLA-B Genotypes and Phenytoin Dosing: 2020 Update. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2021. PMID:32779747
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
- Dutch Pharmacogenetics Working Group (DPWG) guideline for the gene-drug interaction of CYP2C9, HLA-A and HLA-B with anti-epileptic drugs. European journal of human genetics : EJHG. 2024. PMID:38570725
- Drugs@FDA Drug Product: DILANTIN (phenytoin), NDA008762, Upjohn.
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
pimozide
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Dosing Info
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
The risk of QT-prolongation – and thereby also the risk of torsade de points – is theoretically increased, because the genetic variation results in an increase in the plasma concentration of pimozide. The elevated plasma concentration and associated theoretical increased risk of QT elongation can be negated by following the dose recommendations provided below. |
Use no more than the following doses (80% of the normal maximum dose):
|
Unspecified | |
|
FDA Label Annotation 1 |
Genotype
CYP2D6:*1/*3
|
|
|||
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotype
CYP2D6:*1/*3
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Dutch Pharmacogenetics Working Group (DPWG) guideline for the gene-drug interaction between CYP2D6, CYP3A4 and CYP1A2 and antipsychotics. European journal of human genetics : EJHG. 2024. PMID:37002327
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product ORAP (Pimozide), NDA017473, Teva Select Brands.
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
piroxicam
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer Activity Score
2.0 |
CYP2C9: Normal metabolism | Initiate therapy with recommended starting dose. In accordance with the prescribing information, use the lowest effective dosage for shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals. | Strong | |
|
FDA Label Annotation 1 |
Genotype
CYP2C9:*1/*1
|
|
|||
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotype
CYP2C9:*1/*1
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline (CPIC) for CYP2C9 and Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2020. PMID:32189324
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product Feldene (piroxicam), NDA018147, Pfizer Laboratories Div Pfizer Inc.
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
pitavastatin
In case no genotype can be determined, recommendations are based on the rs4149056 genotype alone as per guideline. The minor C allele at rs4149056 defines SLCO1B1*5.
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Function |
SLCO1B1: Typical myopathy risk and statin exposure |
Prescribe desired starting dose and adjust doses based on disease-specific guidelines.
Other ConsiderationsThe potential for drug-drug interactions and dose limits based on renal and hepatic function and ancestry should be evaluated prior to initiating a statin. |
Strong |
Citations:
- The Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline for SLCO1B1, ABCG2, and CYP2C9 genotypes and Statin-Associated Musculoskeletal Symptoms. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2022. PMID:35152405
pravastatin
In case no genotype can be determined, recommendations are based on the rs4149056 genotype alone as per guideline. The minor C allele at rs4149056 defines SLCO1B1*5.
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Function |
SLCO1B1: Typical myopathy risk and statin exposure |
Prescribe desired starting dose and adjust doses based on disease-specific guidelines.
Other ConsiderationsThe potential for drug-drug interactions and dose limits based on renal and hepatic function and ancestry should be evaluated prior to initiating a statin. |
Strong |
Citations:
- The Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline for SLCO1B1, ABCG2, and CYP2C9 genotypes and Statin-Associated Musculoskeletal Symptoms. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2022. PMID:35152405
primaquine
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal |
G6PD: Low risk of acute hemolytic anemia | No reason to avoid based on G6PD status | Strong | |
|
FDA Label Annotation 1 |
Genotype
G6PD:B (reference)/B (reference)
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Expanded Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline for Medication Use in the Context of G6PD Genotype. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2023. PMID:36049896
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product Primaquine Phosphate (Primaquine Phosphate), NDA008316, PD-Rx Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
propafenone
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Alternate Drug
Other Guidance
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
Genetic variation increases the sum of the plasma concentrations of propafenone and the active metabolite 5-hydroxypropafenone. This may increase the risk of side effects. |
It is not possible to offer adequately substantiated recommendations for dose adjustment based on the literature.
|
Unspecified | |
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotype
CYP2D6:*1/*3
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
quetiapine
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer |
The guideline does not provide a description of the impact of a normal metabolizer phenotype on quetiapine. | The guideline does not provide a recommendation for quetiapine in normal metabolizers. | No recommendation |
Citations:
- Dutch Pharmacogenetics Working Group (DPWG) guideline for the gene-drug interaction between CYP2D6, CYP3A4 and CYP1A2 and antipsychotics. European journal of human genetics : EJHG. 2024. PMID:37002327
rasburicase
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal |
G6PD: Low risk of acute hemolytic anemia | No reason to avoid based on G6PD status | Strong | |
|
FDA Label Annotation 1 |
Genotype
G6PD:B (reference)/B (reference)
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) guidelines for rasburicase therapy in the context of G6PD deficiency genotype. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2014. PMID:24787449
- Expanded Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline for Medication Use in the Context of G6PD Genotype. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2023. PMID:36049896
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product Elitek (rasburicase), BLA103946, sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC.
risperidone
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
There is little evidence to support an increase in side effects caused by the gene variation. The gene variation may lead to a decrease in the required maintenance dose. However, as the effect on the dose is smaller than that of the normal biological variation, action is not useful. | NO action is needed for this gene-drug interaction. | Unspecified | |
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotype
CYP2D6:*1/*3
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
- Dutch Pharmacogenetics Working Group (DPWG) guideline for the gene-drug interaction between CYP2D6, CYP3A4 and CYP1A2 and antipsychotics. European journal of human genetics : EJHG. 2024. PMID:37002327
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
rosuvastatin
In case no genotype can be determined, recommendations are based on the rs4149056 genotype alone as per guideline. The minor C allele at rs4149056 defines SLCO1B1*5.
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotypes
|
|
Prescribe desired starting dose and adjust doses of rosuvastatin based on disease-specific and specific population guidelines.
Other ConsiderationsThe potential for drug-drug interactions and dose limits based on renal and hepatic function and Asian ancestry should be evaluated prior to initiating rosuvastatin. |
Strong | |
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Function |
The guideline does not provide a recommendation for rosuvastatin in patients with the SLCO1B1 521 TT genotype | No recommendation | ||
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotype
SLCO1B1:*1/*1
|
|
|||
Citations:
- The Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline for SLCO1B1, ABCG2, and CYP2C9 genotypes and Statin-Associated Musculoskeletal Symptoms. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2022. PMID:35152405
- Dutch Pharmacogenetics Working Group (DPWG) guideline for the gene-drug interaction between SLCO1B1 and statins and CYP2C9 and sulfonylureas. European journal of human genetics : EJHG. 2024. PMID:39676086
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
sertraline
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotypes
|
|
Initiate therapy with recommended starting dose. | Strong | |
|
DPWG Guideline Annotation 1 |
Genotype
CYP2C19:*38/*38
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 Genotypes and Dosing of Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2015. PMID:25974703
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for CYP2D6, CYP2C19, CYP2B6, SLC6A4, and HTR2A Genotypes and Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor Antidepressants. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2023. PMID:37032427
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
- Dutch Pharmacogenetics Working Group (DPWG) guideline for the gene-drug interaction between CYP2C19 and CYP2D6 and SSRIs. European journal of human genetics : EJHG. 2022. PMID:34782755
sevoflurane
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Other Guidance
|
Genotype
Phenotypes
|
These results do not eliminate the chance that this patient is susceptible to malignant hyperthermia (MH). The genetic cause of about half of all MH survivors, with MH susceptibility confirmed by contracture test, remains unknown (PMID 28902675). | Clinical findings, family history, further genetic testing and other laboratory data should guide use of halogenated volatile anesthetics or depolarizing muscle relaxants. | Strong |
|
Population: Alternate Drug
|
Genotype
Phenotypes
|
"CONTRAINDICATIONS: Known or suspected genetic susceptibility to malignant hyperthermia...ULTANE [sevoflurane] can induce malignant hyperthermia in patients with known or suspected susceptibility based on genetic factors or family history, including those with certain inherited ryanodine receptor (RYR1) or dihydropyridine receptor (CACNA1S) variants." See label for more information. * | Unspecified |
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for the Use of Potent Volatile Anesthetic Agents and Succinylcholine in the Context of RYR1 or CACNA1S Genotypes. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2019. PMID:30499100
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product Ultane (Sevoflurane), NDA020478, AbbVie Inc.
simvastatin
In case no genotype can be determined, recommendations are based on the rs4149056 genotype alone as per guideline. The minor C allele at rs4149056 defines SLCO1B1*5.
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Function |
SLCO1B1: Typical myopathy risk and statin exposure |
Prescribe desired starting dose and adjust doses based on disease-specific guidelines.
Other ConsiderationsThe potential for drug-drug interactions and dose limits based on renal and hepatic function and ancestry should be evaluated prior to initiating a statin. |
Strong | |
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Function |
The guideline does not provide a description of the impact of the SLCO1B1 521 TT genotype on simvastatin. | The guideline does not provide a recommendation for atorvastatin in patients with the SLCO1B1 521 TT genotype. | No recommendation | |
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotype
SLCO1B1:*1/*1
|
|
|||
Citations:
- The clinical pharmacogenomics implementation consortium: CPIC guideline for SLCO1B1 and simvastatin-induced myopathy. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2012. PMID:22617227
- The clinical pharmacogenetics implementation consortium guideline for SLCO1B1 and simvastatin-induced myopathy: 2014 update. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2014. PMID:24918167
- The Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline for SLCO1B1, ABCG2, and CYP2C9 genotypes and Statin-Associated Musculoskeletal Symptoms. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2022. PMID:35152405
- Dutch Pharmacogenetics Working Group (DPWG) guideline for the gene-drug interaction between SLCO1B1 and statins and CYP2C9 and sulfonylureas. European journal of human genetics : EJHG. 2024. PMID:39676086
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
siponimod
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer |
The guideline does not provide a description of the impact of a normal metabolizer phenotype on siponimod. | The guideline does not provide a recommendation for siponimod in normal metabolizers. | No recommendation | |
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer Activity Score
2.0 |
The MAYZENT (siponimod) label states: "Recommended Dosage in Patients With CYP2C9 Genotypes *1/*1, *1/*2, or *2/*2" "Initiate MAYZENT with a 5-day titration, as shown in Table 1... A starter pack should be used for patients who will be titrated to the 2-mg maintenance dosage" "After treatment titration (see Treatment Initiation), the recommended maintenance dosage of MAYZENT is 2 mg taken orally once daily starting on Day 6." See label for more information. * | Unspecified | ||
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotype
CYP2C9:*1/*1
|
|
|||
succinylcholine
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Other Guidance
|
Genotype
Phenotypes
|
These results do not eliminate the chance that this patient is susceptible to malignant hyperthermia (MH). The genetic cause of about half of all MH survivors, with MH susceptibility confirmed by contracture test, remains unknown (PMID 28902675). | Clinical findings, family history, further genetic testing and other laboratory data should guide use of halogenated volatile anesthetics or depolarizing muscle relaxants. | Strong |
|
Population: Alternate Drug
Other Guidance
|
Genotype
Phenotypes
|
"ANECTINE [succinylcholine] is contraindicated in patients with...[k]nown or suspected genetic susceptibility to malignant hyperthermia...Anectine [succinylcholine] can induce malignant hyperthermia in patients with known or suspected susceptibility based on genetic factors or family history, including those with certain inherited ryanodine receptor (RYR1) or dihydropyridine receptor (CACNA1S) variants...Succinylcholine is metabolized by plasma cholinesterase and should be used with caution, if at all, in patients known to be or suspected of being homozygous for the atypical plasma cholinesterase gene [BCHE] ." See label for more information. * | Unspecified |
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for the Use of Potent Volatile Anesthetic Agents and Succinylcholine in the Context of RYR1 or CACNA1S Genotypes. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2019. PMID:30499100
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product Anectine (Succinylcholine Chloride), NDA008453, Sandoz Inc.
tacrolimus
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Dosing Info
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer |
CYP3A5: Lower dose-adjusted trough concentrations of tacrolimus and decreased chance of achieving target tacrolimus concentrations. |
Increase starting dose 1.5 to 2 times recommended starting dose. Total starting dose should not exceed 0.3 mg/kg/day. Use therapeutic drug monitoring to guide dose adjustments.
Other ConsiderationsThis recommendation includes the use of tacrolimus in kidney, heart, lung and hematopoietic stem cell transplant patients, and liver transplant patients where the donor and recipient genotypes are identical. Further dose adjustments or selection of alternative therapy may be necessary due to other clinical factors (e.g., medication interactions, or hepatic function). Typically with other CYP enzymes, a normal metabolizer would be classified as having normal metabolism, and therefore, the drug dose would not change based on the patient’s genotype. However, in the case of CYP3A5 and tacrolimus, a CYP3A5 expresser (i.e., CYP3A5 normal metabolizer or intermediate metabolizer) would require a higher recommended starting dose, and the CYP3A5 non-expresser (i.e., poor metabolizer) would require the standard recommended starting dose. |
Strong |
|
Population: Dosing Info
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer |
An increase of the initial dose can result in an increased chance of reaching a tacrolimus concentration within the target range before the start of therapeutic drug monitoring. However, there is no direct evidence that this results in improved clinical results. The genetic variation results in an increased conversion of tacrolimus to inactive metabolites and therefore a higher required dose. | LIVER TRANSPLANTATION In addition to the patient’s genotype, the metabolism of tacrolimus is also determined by the genotype of the transplanted liver. LIVER is also of the genotype HOMOZYGOUS EXPRESSOR: Use 2.5 times the normal initial dose. Adjustment of the dose should then be based on therapeutic drug monitoring. LIVER has a DIFFERENT genotype: There is insufficient evidence in the literature to support a dose recommendation. OTHER TRANSPLANTATION Use 2.5 times the initial dose that would yield the desired result in non-expressers. Adjustment of the dose should then be based on therapeutic drug monitoring. For example: One Dutch study found a median trough concentration for tacrolimus after three days of 9.4 ng/mL at an initial dose of 0.15 mg/kg twice daily for 5 homozygous kidney transplant patients. Their target value was 10 - 15 ng/mL. | Unspecified |
|
Affected subgroup: CYP3A5 intermediate or normal metabolizers Dosing Info
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer |
"Results in lower systemic concentrations, lower probability of achieving target concentrations and may result in higher rejection risk. Measure drug concentrations and adjust dosage based on trough whole blood tacrolimus concentrations." * | Unspecified |
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guidelines for CYP3A5 Genotype and Tacrolimus Dosing. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2015. PMID:25801146
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
tafenoquine
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal |
G6PD: Low risk of acute hemolytic anemia |
No reason to avoid based on G6PD status
Other ConsiderationsTafenoquine’s safety has been established for a G6PD enzyme activity ≥70% of normal. (Inclusion criteria for clinical trials involving tafenoquine included G6PD activity ≥70%.) |
Strong | |
|
FDA Label Annotation 1 |
Genotype
G6PD:B (reference)/B (reference)
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) guidelines for rasburicase therapy in the context of G6PD deficiency genotype. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2014. PMID:24787449
- Expanded Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline for Medication Use in the Context of G6PD Genotype. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2023. PMID:36049896
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product Arakoda (Tafenoquine), NDA210607, 60 Degrees Pharmaceuticals, LLC.
tamoxifen
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Alternate Drug
Dosing Info
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
CYP2D6: Lower endoxifen concentrations compared to normal metabolizers; higher risk of breast cancer recurrence, event-free and recurrence-free survival compared to normal metabolizers. | Consider hormonal therapy such as an aromatase inhibitor for postmenopausal women or aromatase inhibitor along with ovarian function suppression in premenopausal women, given that these approaches are superior to tamoxifen regardless of CYP2D6 genotype (PMID 26211827). If aromatase inhibitor use is contraindicated, consideration should be given to use a higher but FDA approved tamoxifen dose (40 mg/day)(PMID 27226358). Avoid CYP2D6 strong to weak inhibitors. | Optional |
|
Population: Alternate Drug
Dosing Info
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
This gene variation reduces the conversion of tamoxifen to the active metabolite endoxifen. This can result in reduced effectiveness. |
|
Unspecified |
|
Affected subgroup: CYP2D6 intermediate or poor metabolizers No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
"Results in lower systemic active metabolite concentrations. The impact of CYP2D6 intermediate or poor metabolism on efficacy is not well established." * | Unspecified |
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for CYP2D6 and Tamoxifen Therapy. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2018. PMID:29385237
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
tegafur
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
2.0 (Normal Metabolizer) |
The guideline does not provide a description of the impact of a DPYD activity score of 2 on tegafur. | The guideline does not provide a recommendation for tegafur in patients with a DPYD activity score of 2. | No recommendation |
Citations:
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
- Dutch Pharmacogenetics Working Group (DPWG) guideline for the gene-drug interaction of DPYD and fluoropyrimidines. European journal of human genetics : EJHG. 2020. PMID:31745289
tenoxicam
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer Activity Score
2.0 |
CYP2C9: Normal metabolism | Initiate therapy with recommended starting dose. In accordance with the prescribing information, use the lowest effective dosage for shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals. | Strong |
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline (CPIC) for CYP2C9 and Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2020. PMID:32189324
tetrabenazine
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Dosing Info
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
"Genotyped patients who are identified as extensive (EMs) or intermediate metabolizers (IMs) of CYP2D6, who need doses of XENAZINE [tetrabenazine] above 50 mg per day, should be titrated up slowly at weekly intervals by 12.5 mg daily, to allow the identification of a tolerated dose that reduces chorea. Doses above 50 mg per day should be given in a three times a day regimen. The maximum recommended daily dose is 100 mg and the maximum recommended single dose is 37.5 mg. If adverse reactions such as akathisia, parkinsonism, depression, insomnia, anxiety or sedation occur, titration should be stopped and the dose should be reduced. If the adverse reaction does not resolve, consideration should be given to withdrawing XENAZINE [tetrabenazine] treatment or initiating other specific treatment." See label for more information * | Unspecified | ||
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotype
CYP2D6:*1/*3
|
|
|||
thioguanine
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotypes
|
|
Start with normal starting dose (e.g., 40-60 mg/m2/day) and adjust doses of thioguanine and of other myelosuppressive therapy without any special emphasis on thioguanine. Allow 2 weeks to reach steady-state after each dose adjustment (PMID 20354201, 11037857).
Other ConsiderationsNormal starting doses vary by race/ethnicity and treatment regimens. If standard dose is below normal recommended dose, dose reduction might not be recommended for intermediate metabolizers. |
Strong | |
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer |
The guideline does not provide a description of the impact of a normal metabolizer phenotype on thioguanine. | The guideline does not provide a recommendation for thioguanine in normal metabolizers | No recommendation | |
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer |
The guideline does not provide a description of the impact of a normal metabolizer phenotype on thioguanine. | The guideline does not provide a recommendation for thioguanine in normal metabolizers. | No recommendation | |
|
FDA Label Annotation 1 |
Genotypes
NUDT15:*1/*1;TPMT:*1/*1 |
|
|||
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotypes
NUDT15:*1/*1;TPMT:*1/*1 |
|
|||
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guidelines for thiopurine methyltransferase genotype and thiopurine dosing. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21270794
- Clinical pharmacogenetics implementation consortium guidelines for thiopurine methyltransferase genotype and thiopurine dosing: 2013 update. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2013. PMID:23422873
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline for Thiopurine Dosing Based on TPMT and NUDT15 Genotypes: 2018 Update. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2019. PMID:30447069
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product TABLOID (thioguanine), NDA012429, Aspen Global Inc.
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
thioridazine
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Alternate Drug
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
"...thioridazine is contraindicated...in patients, comprising about 7% of the normal population, who are known to have a genetic defect leading to reduced levels of activity of P450 2D6." See label for more information. * | Unspecified | ||
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotype
CYP2D6:*1/*3
|
|
|||
toluidine blue
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal |
G6PD: Low risk of acute hemolytic anemia |
No reason to avoid based on G6PD status
Other ConsiderationsToluidine blue classification strength is based on extrapolation from methylene blue data |
Strong |
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) guidelines for rasburicase therapy in the context of G6PD deficiency genotype. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2014. PMID:24787449
- Expanded Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline for Medication Use in the Context of G6PD Genotype. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2023. PMID:36049896
tramadol
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Other Guidance
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
CYP2D6: Reduced O-desmethyltramadol (active metabolite) formation | Use tramadol label recommended age- or weight-specific dosing. If no response and opioid use is warranted, consider non-codeine opioid. | Optional | |
|
Population: Alternate Drug
Dosing Info
Other Guidance
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
The genetic variation reduces the conversion of tramadol to a metabolite with a higher activity. This can result in reduced analgesia. |
It is not possible to provide a recommendation for dose adjustment, because the total analgesic effect changes when the ratio between the mother compound and the active metabolite changes.
|
Unspecified | |
|
FDA Label Annotation 1 |
Genotype
CYP2D6:*1/*3
|
|
|||
|
Genotype
CYP2D6:*1/*3
|
|
||||
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline for CYP2D6, OPRM1, and COMT Genotypes and Select Opioid Therapy. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2021. PMID:33387367
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
- Dutch Pharmacogenetics Working Group (DPWG) guideline for the gene-drug interaction between CYP2D6 and opioids (codeine, tramadol and oxycodone). European journal of human genetics : EJHG. 2022. PMID:34267337
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product ULTRAM (tramadol hydrochloride), NDA020281, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
trimipramine
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Dosing Info
|
Genotype
Phenotypes
Activity Scores
|
|
Consider a 25% reduction of recommended starting dose. Utilize therapeutic drug monitoring to guide dose adjustments.
Other ConsiderationsPatients may receive an initial low dose of a tricyclic, which is then increased over several days to the recommended steady-state dose. The starting dose in this guideline refers to the recommended steady-state dose. Dosing recommendations only apply to higher initial doses of TCAs for treatment of conditions such as depression. See other considerations for dosing recommendations for conditions where lower initial doses are used, such as neuropathic pain. |
Optional |
|
Affected subgroup: CYP2D6 ultrarapid, intermediate, or poor metabolizers No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
"May alter systemic concentrations." * | Unspecified |
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guideline for CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 genotypes and dosing of tricyclic antidepressants. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2013. PMID:23486447
- Clinical pharmacogenetics implementation consortium guideline (CPIC) for CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 genotypes and dosing of tricyclic antidepressants: 2016 update. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2017. PMID:27997040
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
tropisetron
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
CYP2D6: Very limited data available for CYP2D6 intermediate metabolizers |
Insufficient evidence demonstrating clinical impact based on CYP2D6 genotype. Initiate therapy with recommended starting dose.
Other ConsiderationsDrug-drug interactions and other patient characteristics (e.g., age, renal function, and liver function) should be considered when selecting alternative therapy. |
No recommendation |
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) guideline for CYP2D6 genotype and use of ondansetron and tropisetron. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2017. PMID:28002639
venlafaxine
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
CYP2D6: Decreased metabolism of venlafaxine to active metabolite O-desmethylvenlafaxine (desvenlafaxine) and decreased O-desmethylvenlafaxine:venlafaxine ratio as compared to normal metabolizers. There is insufficient evidence supporting the clinical impact of the decreased O-desmethylvenlafaxine:venlafaxine ratio in CYP2D6 intermediate metabolizers. | No action recommended based on genotype for venlafaxine because of minimal evidence regarding the impact on efficacy or side effects. | No recommendation | |
|
Population: Alternate Drug
Dosing Info
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
There are indications of an increased risk of side effects and a reduced chance of efficacy. The gene variation reduces the conversion of venlafaxine to the active metabolite O-desmethylvenlafaxine, whilst an association between high O-desmethylvenlafaxine/venlafaxine ratios and response without side effects was found. |
It is not possible to offer adequately substantiated advice for dose reduction based on the literature.
|
Unspecified | |
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotype
CYP2D6:*1/*3
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for CYP2D6, CYP2C19, CYP2B6, SLC6A4, and HTR2A Genotypes and Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor Antidepressants. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2023. PMID:37032427
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
- Dutch Pharmacogenetics Working Group (DPWG) guideline for the gene-drug interaction between CYP2D6, CYP2C19 and non-SSRI/non-TCA antidepressants. European journal of human genetics : EJHG. 2024. PMID:38956296
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
voriconazole
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer |
CYP2C19: Normal voriconazole metabolism |
Initiate therapy with recommended standard of care dosing
Other ConsiderationsFurther dose adjustments or selection of alternative therapy may be necessary due to other clinical factors, such as drug interactions, hepatic function, renal function, species, site of infection, therapeutic drug monitoring, and comorbidities. |
Strong | |
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer |
CYP2C19: Normal voriconazole metabolism |
Initiate therapy with recommended standard of care dosing
Other ConsiderationsFurther dose adjustments or selection of alternative therapy may be necessary due to other clinical factors, such as drug interactions, hepatic function, renal function, species, site of infection, therapeutic drug monitoring, and comorbidities. |
Strong | |
|
DPWG Guideline Annotation 1 |
Genotype
CYP2C19:*38/*38
|
|
|||
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotype
CYP2C19:*38/*38
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guidelines for CYP2C19 and Voriconazole Therapy. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2017. PMID:27981572
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
vortioxetine
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
CYP2D6: Reduced metabolism of vortioxetine to less active compounds when compared to CYP2D6 normal metabolizers. Higher plasma concentrations may increase the probability of side effects. | Initiate therapy with recommended starting dose. | Moderate | |
|
FDA Label Annotation 1 |
Genotype
CYP2D6:*1/*3
|
|
|||
|
FDA PGx Association 1 |
Genotype
CYP2D6:*1/*3
|
|
|||
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for CYP2D6, CYP2C19, CYP2B6, SLC6A4, and HTR2A Genotypes and Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor Antidepressants. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2023. PMID:37032427
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product Trintellix (vortioxetine), NDA204447, Cardinal Health.
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
warfarin
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: |
Genotype
|
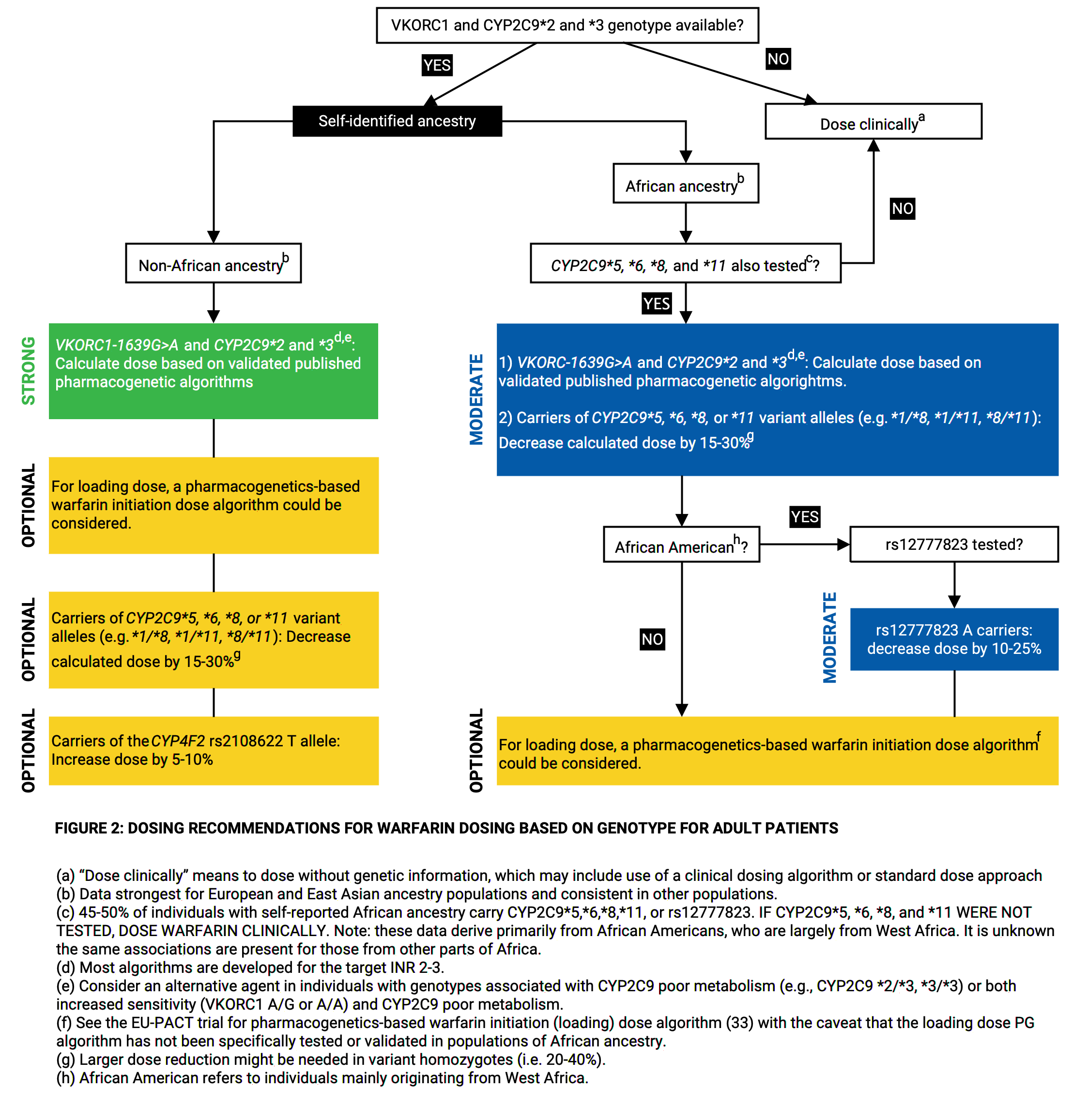
|
|||
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer |
The guideline does not provide a description of the impact of a normal metabolizer phenotype on warfarin. | The guideline does not provide a recommendation for warfarin in normal metabolizers. | No recommendation | |
|
Population: No Action
|
Genotype
Phenotype
-1639 GG |
The guideline does not provide a description of the impact of the VKORC1 rs9923231 CC genotype (-1639 GG genotype) on warfarin. | The guideline does not provide a recommendation for warfarin in patients with the VKORC1 rs9923231 CC genotype (-1639 GG genotype). | No recommendation | |
|
Population: Dosing Info
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Normal Metabolizer Activity Scores
|
Table 1 in the drug label provides ranges of expected maintenance daily doses of warfarin (COUMADIN) based on CYP2C9*2, CYP2C9*3 and VKORC1−1639G>A (rs9923231) genotypes. For CYP2C9*1/*1, VKORC1 GG (rs9923231CC), the range of expected maintenance daily dose is 5-7 mg. * | Unspecified | ||
|
Genotypes
CYP2C9:*1/*1;VKORC1:rs9923231 reference (C)/rs9923231 reference (C) |
|
||||
Citations:
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guidelines for CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genotypes and warfarin dosing. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21900891
- Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for Pharmacogenetics-Guided Warfarin Dosing: 2017 Update. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2017. PMID:28198005
- Drugs@FDA: Drug Product COUMADIN (warfarin sodium), NDA009218, Bristol-Myers Squibb Pharma Company.
- FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations.
zuclopenthixol
| Source | Genes | Implications | Recommendation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Population: Dosing Info
|
Genotype
Phenotype
Intermediate Metabolizer Activity Score
1.0 |
The risk of side effects may be elevated. The genetic variation leads to decreased conversion of zuclopentixol, which causes the plasma concentration to be approximately 1.35-fold higher. | Use 75% of the normal dose. | Unspecified |
Citations:
- Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte--an update of guidelines. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2011. PMID:21412232
- Dutch Pharmacogenetics Working Group (DPWG) guideline for the gene-drug interaction between CYP2D6, CYP3A4 and CYP1A2 and antipsychotics. European journal of human genetics : EJHG. 2024. PMID:37002327
Drugs With No Guidance
The following drugs are known to be associated with genes in this report but have no guidance for the specific genotypes in this report. For more information, see the "Prescribing Info" page on PharmGKB.
- Ascorbic acid (vitamin C), combinations
- Ascorbic acid (vitamin C), plain
- abrocitinib
- acetaminophen / caffeine / dihydrocodeine
- amikacin
- amphetamine
- aripiprazole lauroxil
- articaine / epinephrine
- avatrombopag
- belinostat
- belzutifan
- brivaracetam
- bupivacaine
- carisoprodol
- carvedilol
- cevimeline
- chloroquine
- chlorpropamide
- clobazam
- clozapine
- dabrafenib
- darifenacin
- deuruxolitinib
- deutetrabenazine
- dextromethorphan / quinidine
- dextromethorphan hydrobromide / bupropion hydrochloride
- diazepam
- dibekacin
- dolutegravir
- donepezil
- dronabinol
- elagolix
- erdafitinib
- esomeprazole
- fesoterodine
- flibanserin
- fluoxetine
- flutamide
- galantamine
- gefitinib
- gentamicin
- glimepiride
- glipizide
- glyburide
- hydroxychloroquine
- iloperidone
- kanamycin
- lesinurad
- lidocaine / prilocaine
- lidocaine and tetracaine
- lofexidine
- mavacamten
- mepivacaine
- metoclopramide
- mirabegron
- moviprep
- nalidixic acid
- nateglinide
- nebivolol
- neomycin
- netilmicin
- nilotinib
- oliceridine
- oxymetazoline and tetracaine
- paromomycin
- peginterferon alfa-2a
- peginterferon alfa-2b
- perphenazine
- pitolisant
- plazomicin
- propranolol
- protriptyline
- rabeprazole
- raltegravir
- ribavirin
- ribostamycin
- ropivacaine
- sacituzumab govitecan
- sodium ascorbate
- sodium nitrite
- streptomycin
- sulfasalazine
- tamsulosin
- tobramycin
- tolazamide
- tolbutamide
- tolterodine
- valbenazine
- viloxazine
Section III: Allele Matching Details
- ABCG2 allele match data
- CACNA1S allele match data
- CFTR allele match data
- CYP2B6 allele match data
- CYP2C19 allele match data
- CYP2C9 allele match data
- CYP2D6 allele match data
- CYP3A4 allele match data
- CYP3A5 allele match data
- CYP4F2 allele match data
- DPYD allele match data
- G6PD allele match data
- HLA-B allele match data
- IFNL3/4 allele match data
- MT-RNR1 allele match data
- NUDT15 allele match data
- RYR1 allele match data
- SLCO1B1 allele match data
- TPMT allele match data
- UGT1A1 allele match data
- VKORC1 allele match data
ABCG2 allele match data
| Variant Matched: | rs2231142 reference (G)/rs2231142 reference (G) |
|---|---|
| Phasing Status: |
Unphased PharmCAT reports the genotype(s) that receive the highest score during the matcher process. In case of unphased data, additional genotypes might be possible and cannot be ruled out. |
Calls at Positions
| Position in VCF | RSID | Call in VCF | Reference | Related Alleles and Function | Warnings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| chr4:88131171 | rs2231142 | G/G | G |
|
CACNA1S allele match data
| Variant Matched: | Reference/Reference |
|---|---|
| Phasing Status: |
Unphased PharmCAT reports the genotype(s) that receive the highest score during the matcher process. In case of unphased data, additional genotypes might be possible and cannot be ruled out. |
Calls at Positions
| Position in VCF | RSID | Call in VCF | Reference | Related Alleles and Function | Warnings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| chr1:201060815 | rs1800559 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr1:201091993 | rs772226819 | G/G | G |
|
CFTR allele match data
| Variant Matched: | Reference/Reference |
|---|---|
| Phasing Status: |
Unphased PharmCAT reports the genotype(s) that receive the highest score during the matcher process. In case of unphased data, additional genotypes might be possible and cannot be ruled out. |
Calls at Positions
| Position in VCF | RSID | Call in VCF | Reference | Related Alleles and Function | Warnings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| chr7:117509035 | rs397508256 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr7:117509069 | rs368505753 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr7:117509089 | rs115545701 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr7:117530953 | rs113993958 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr7:117530955 | rs397508537 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr7:117530974 | rs77834169 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr7:117530975 | rs78655421 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr7:117534318 | rs80282562 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr7:117534363 | rs397508759 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr7:117534368 | rs397508761 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr7:117535285 | rs121908752 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr7:117540270 | rs77932196 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr7:117540285 | rs121908753 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr7:117548795 | rs74551128 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr7:117587799 | rs121908757 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr7:117587800 | rs121908755 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr7:117587801 | rs121909005 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr7:117587805 | rs121909013 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr7:117587806 | rs75527207 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr7:117590409 | rs397508288 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr7:117594930 | rs397508387 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr7:117602868 | rs80224560 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr7:117603708 | rs397508442 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr7:117606695 | rs141033578 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr7:117611555 | rs76151804 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr7:117611595 | rs150212784 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr7:117611620 | rs397508513 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr7:117611640 | rs121909020 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr7:117611646 | rs200321110 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr7:117611649 | rs202179988 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr7:117611650 | rs78769542 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr7:117611663 | rs186045772 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr7:117614699 | rs75541969 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr7:117639961 | rs75039782 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr7:117642451 | rs267606723 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr7:117642472 | rs74503330 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr7:117642483 | rs121909041 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr7:117642528 | rs11971167 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr7:117664770 | rs193922525 | G/G | G |
|
CYP2B6 allele match data
| Allele Matched: | *1/*1 |
|---|---|
| Phasing Status: |
Unphased PharmCAT reports the genotype(s) that receive the highest score during the matcher process. In case of unphased data, additional genotypes might be possible and cannot be ruled out. |
Calls at Positions
| Position in VCF | RSID | Call in VCF | Reference | Related Alleles and Function | Warnings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| chr19:40991224 | rs34223104 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:40991367 | rs34883432 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:40991369 | rs8192709 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:40991381 | rs33973337 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:40991388 | rs33980385 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:40991390 | rs33926104 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:40991391 | rs34284776 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:40991441 | rs35303484 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:41004015 | rs281864907 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:41004125 | rs36060847 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:41004133 | rs148009906 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:41004158 | rs186335453 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:41004303 | rs139801276 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:41004377 | rs12721655 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:41004380 | rs535039125 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:41004381 | rs35773040 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:41004406 | rs145884402 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:41004435 | rs141666881 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:41006919 | rs3826711 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:41006923 | rs36056539 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:41006936 | rs3745274 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:41006967 | rs58871670 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:41006968 | rs373489637 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:41007013 | rs36079186 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:41009313 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chr19:41009350 | rs45482602 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:41009358 | rs2279343 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:41010006 | rs139029625 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:41010088 | rs34698757 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:41010108 | rs193922917 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:41012316 | rs28399499 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:41012339 | rs34826503 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:41012393 | rs754621576 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:41012394 | rs780991919 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:41012465 | rs34097093 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:41012466 | rs200458614 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:41012471 | rs201500445 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:41012478 | rs200238771 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:41012693 | rs35979566 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:41012740 | rs193922918 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:41012803 | rs35010098 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:41016652 | rs764288403 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:41016679 | rs374099483 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:41016726 | rs3211369 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:41016741 | rs117872433 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:41016778 | rs564083989 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:41016805 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chr19:41016810 | rs3211371 | C/C | C |
|
CYP2C19 allele match data
| Allele Matched: | *38/*38 |
|---|---|
| Phasing Status: |
Unphased PharmCAT reports the genotype(s) that receive the highest score during the matcher process. In case of unphased data, additional genotypes might be possible and cannot be ruled out. |
Calls at Positions
| Position in VCF | RSID | Call in VCF | Reference | Related Alleles and Function | Warnings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| chr10:94761900 | rs12248560 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr10:94762706 | rs28399504 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr10:94762712 | rs367543002 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr10:94762715 | rs367543003 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr10:94762755 | rs55752064 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr10:94762760 | rs17882687 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr10:94762788 | rs1564656981 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr10:94762856 | rs1564657013 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr10:94775106 | rs145328984 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr10:94775121 | rs1564660997 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr10:94775160 | rs118203756 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr10:94775185 | rs1288601658 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr10:94775367 | rs12769205 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr10:94775416 | rs41291556 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr10:94775423 | rs17885179 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr10:94775453 | rs72552267 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr10:94775489 | rs17884712 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr10:94775507 | rs58973490 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr10:94780574 | rs140278421 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr10:94780579 | rs370803989 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr10:94780653 | rs4986893 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr10:94781858 | rs6413438 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr10:94781859 | rs4244285 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr10:94781944 | rs375781227 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr10:94781999 | rs72558186 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr10:94842861 | rs138142612 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr10:94842866 | rs3758581 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr10:94842879 | rs118203757 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr10:94842995 | rs113934938 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr10:94849995 | rs17879685 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr10:94852738 | rs56337013 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr10:94852765 | rs192154563 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr10:94852785 | rs118203759 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr10:94852914 | rs55640102 | A/A | A |
|
CYP2C9 allele match data
| Allele Matched: | *1/*1 |
|---|---|
| Phasing Status: |
Unphased PharmCAT reports the genotype(s) that receive the highest score during the matcher process. In case of unphased data, additional genotypes might be possible and cannot be ruled out. |
Calls at Positions
| Position in VCF | RSID | Call in VCF | Reference | Related Alleles and Function | Warnings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| chr10:94938683 | rs114071557 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr10:94938719 | T/T | T |
|
||
| chr10:94938737 | rs67807361 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr10:94938771 | rs142240658 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr10:94938788 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chr10:94938800 | rs1364419386 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr10:94938803 | rs2031308986 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr10:94938828 | rs564813580 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr10:94941897 | rs371055887 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr10:94941915 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chr10:94941958 | rs72558187 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr10:94941975 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chr10:94941976 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chr10:94941982 | rs762239445 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr10:94942018 | T/T | T |
|
||
| chr10:94942205 | rs1304490498 | CAATGGAAA GA/ CAATGGAAA GA |
CAATGGAAA GA |
|
|
| chr10:94942216 | rs774607211 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr10:94942230 | rs767576260 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr10:94942231 | rs12414460 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr10:94942233 | rs375805362 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr10:94942234 | rs72558189 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr10:94942243 | rs1375956433 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr10:94942249 | rs200965026 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr10:94942254 | rs199523631 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr10:94942255 | rs200183364 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr10:94942290 | rs1799853 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr10:94942291 | rs141489852 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr10:94942305 | rs754487195 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr10:94942306 | rs1289704600 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr10:94942308 | rs17847037 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr10:94942309 | rs7900194 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr10:94947782 | rs72558190 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr10:94947785 | rs774550549 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr10:94947869 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chr10:94947907 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chr10:94947917 | rs1326630788 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr10:94947938 | rs2031531005 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr10:94947939 | rs370100007 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr10:94949129 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chr10:94949144 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chr10:94949145 | rs772782449 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr10:94949161 | AT/AT | AT |
|
||
| chr10:94949217 | rs2256871 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr10:94949280 | rs9332130 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr10:94949281 | rs9332131 | GA/GA | GA |
|
|
| chr10:94972119 | rs182132442 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr10:94972123 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chr10:94972134 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chr10:94972179 | rs72558192 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr10:94972180 | rs988617574 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr10:94972183 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chr10:94972233 | rs1237225311 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr10:94981199 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chr10:94981201 | rs57505750 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr10:94981224 | rs28371685 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr10:94981225 | rs367826293 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr10:94981230 | rs1274535931 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr10:94981250 | rs750820937 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr10:94981258 | rs1297714792 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr10:94981281 | rs749060448 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr10:94981296 | rs1057910 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr10:94981297 | rs56165452 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr10:94981301 | rs28371686 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr10:94981302 | rs1250577724 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr10:94981305 | rs578144976 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr10:94981365 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chr10:94981371 | rs542577750 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr10:94986042 | rs764211126 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr10:94986073 | rs72558193 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr10:94986136 | rs1254213342 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr10:94986174 | rs1441296358 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr10:94988852 | rs776908257 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr10:94988855 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chr10:94988880 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chr10:94988917 | rs769942899 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr10:94988925 | rs202201137 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr10:94988955 | rs767284820 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr10:94988984 | rs781583846 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr10:94989020 | rs9332239 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr10:94989023 | rs868182778 | G/G | G |
|
Other Positions of Interest
| Position in VCF | RSID | Call in VCF |
|---|---|---|
| chr10:94645745 | rs12777823 | G/G |
CYP2D6 allele match data
| Allele Reported: | *1/*3 |
|---|
CYP3A4 allele match data
| Allele Matched: | *1/*1 |
|---|---|
| Phasing Status: |
Unphased PharmCAT reports the genotype(s) that receive the highest score during the matcher process. In case of unphased data, additional genotypes might be possible and cannot be ruled out. |
Calls at Positions
| Position in VCF | RSID | Call in VCF | Reference | Related Alleles and Function | Warnings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| chr7:99758183 | rs67666821 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr7:99758228 | rs1584538410 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr7:99760836 | rs4986913 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr7:99760901 | rs4986910 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr7:99760956 | rs774109750 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr7:99762047 | rs4986909 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr7:99762054 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chr7:99762069 | T/T | T |
|
||
| chr7:99762177 | rs12721629 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr7:99762186 | rs756833413 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr7:99762206 | rs67784355 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr7:99762234 | rs1318364992 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr7:99763877 | rs368296206 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr7:99763909 | rs1303250043 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr7:99763925 | rs201821708 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr7:99764003 | rs28371759 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr7:99766411 | rs4646438 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr7:99766424 | rs1429705359 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr7:99766439 | rs145582851 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr7:99766440 | rs138105638 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr7:99768360 | rs55785340 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr7:99768371 | rs55901263 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr7:99768424 | rs113667357 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr7:99768447 | rs3208361 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr7:99768458 | rs4987161 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr7:99768470 | rs12721627 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr7:99768693 | rs35599367 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr7:99769769 | rs4986908 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr7:99769781 | rs72552798 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr7:99769804 | rs4986907 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr7:99769805 | rs57409622 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr7:99770165 | rs72552799 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr7:99770166 | rs778013004 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr7:99770196 | T/T | T |
|
||
| chr7:99770202 | rs55951658 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr7:99770217 | rs1449865051 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr7:99778079 | rs56324128 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr7:99780036 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chr7:99784018 | rs570051168 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr7:99784038 | rs12721634 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr7:99784075 | rs188389063 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr7:99784078 | rs1226205448 | C/C | C |
|
CYP3A5 allele match data
| Allele Matched: | *1/*1 |
|---|---|
| Phasing Status: |
Unphased PharmCAT reports the genotype(s) that receive the highest score during the matcher process. In case of unphased data, additional genotypes might be possible and cannot be ruled out. |
Calls at Positions
| Position in VCF | RSID | Call in VCF | Reference | Related Alleles and Function | Warnings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| chr7:99652770 | rs41303343 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr7:99660516 | rs28383479 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr7:99665212 | rs10264272 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr7:99672916 | rs776746 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr7:99676198 | rs55817950 | G/G | G |
|
CYP4F2 allele match data
| Allele Matched: | *1/*1 |
|---|---|
| Phasing Status: |
Unphased PharmCAT reports the genotype(s) that receive the highest score during the matcher process. In case of unphased data, additional genotypes might be possible and cannot be ruled out. |
Calls at Positions
| Position in VCF | RSID | Call in VCF | Reference | Related Alleles and Function | Warnings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| chr19:15878779 | rs3093200 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:15878920 | rs4020346 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:15879412 | rs138971789 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:15879621 | rs2108622 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:15886018 | rs145174239 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:15889671 | rs144233412 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:15890405 | rs3093153 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:15892541 | rs145875499 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:15895527 | rs114396708 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:15895560 | rs144455532 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:15897466 | rs201380574 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:15897473 | rs115517770 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:15897566 | rs114099324 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:15897578 | rs3093105 | A/A | A |
|
DPYD allele match data
| Allele Matched: | Reference/Reference |
|---|---|
| Phasing Status: |
Unphased |
Calls at Positions
| Position in VCF | RSID | Call in VCF | Reference | Related Alleles and Function | Warnings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| chr1:97078987 | rs114096998 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr1:97078993 | rs148799944 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr1:97079005 | rs140114515 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr1:97079071 | rs1801268 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr1:97079076 | rs139459586 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr1:97079077 | rs202144771 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr1:97079121 | rs72547601 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr1:97079133 | rs72547602 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr1:97079139 | rs145529148 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr1:97082365 | rs141044036 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr1:97082391 | rs67376798 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr1:97098598 | rs1801267 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr1:97098599 | rs147545709 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr1:97098616 | rs55674432 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr1:97098632 | rs201035051 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr1:97193109 | rs60139309 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr1:97193209 | rs200687447 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr1:97234958 | rs199634007 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr1:97234991 | rs56005131 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr1:97305279 | rs112766203 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr1:97305363 | rs60511679 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr1:97305364 | rs1801160 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr1:97305372 | rs146529561 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr1:97306195 | rs145548112 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr1:97373598 | rs137999090 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr1:97373629 | rs138545885 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr1:97382461 | rs55971861 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr1:97450058 | rs3918290 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr1:97450059 | rs3918289 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr1:97450065 | rs72549303 | TG/TG | TG |
|
|
| chr1:97450068 | rs17376848 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr1:97450168 | rs147601618 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr1:97450187 | rs145773863 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr1:97450189 | rs138616379 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr1:97450190 | rs59086055 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr1:97515784 | rs201615754 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr1:97515787 | rs55886062 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr1:97515839 | rs1801159 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr1:97515851 | rs142619737 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr1:97515865 | rs1801158 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr1:97515889 | rs190951787 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr1:97515923 | rs148994843 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr1:97549565 | rs138391898 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr1:97549600 | rs111858276 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr1:97549609 | rs72549304 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr1:97549681 | rs199549923 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr1:97549713 | rs57918000 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr1:97549726 | rs144395748 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr1:97549735 | rs72975710 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr1:97573785 | rs186169810 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr1:97573805 | rs142512579 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr1:97573821 | rs764666241 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr1:97573839 | rs200064537 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr1:97573863 | rs56038477 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr1:97573881 | rs61622928 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr1:97573918 | rs143815742 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr1:97573919 | rs140602333 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr1:97573943 | rs78060119 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr1:97579893 | rs75017182 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr1:97593238 | rs72549305 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr1:97593289 | rs143154602 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr1:97593322 | rs183385770 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr1:97593343 | rs72549306 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr1:97593379 | rs201018345 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr1:97595083 | rs145112791 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr1:97595088 | rs150437414 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr1:97595149 | rs146356975 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr1:97679170 | rs45589337 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr1:97691776 | rs1801266 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr1:97699399 | rs72549307 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr1:97699430 | rs72549308 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr1:97699474 | rs115232898 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr1:97699506 | rs6670886 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr1:97699533 | rs139834141 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr1:97699535 | rs2297595 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr1:97721542 | rs200562975 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr1:97721650 | rs141462178 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr1:97740400 | rs150385342 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr1:97740410 | rs72549309 | GATGA/ GATGA |
GATGA |
|
|
| chr1:97883329 | rs1801265 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr1:97883352 | rs80081766 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr1:97883353 | rs72549310 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr1:97883368 | rs150036960 | G/G | G |
|
G6PD allele match data
| Variant Matched: | B (reference)/B (reference) |
|---|---|
| Phasing Status: |
Unphased PharmCAT reports the genotype(s) that receive the highest score during the matcher process. In case of unphased data, additional genotypes might be possible and cannot be ruled out. |
Calls at Positions
| Position in VCF | RSID | Call in VCF | Reference | Related Alleles and Function | Warnings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| chrX:154532046 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chrX:154532055 | CTCT/CTCT | CTCT |
|
||
| chrX:154532082 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chrX:154532083 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chrX:154532085 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chrX:154532086 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chrX:154532203 | rs137852348 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chrX:154532231 | T/T | T |
|
||
| chrX:154532245 | rs137852344 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chrX:154532257 | rs72554664 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chrX:154532258 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chrX:154532264 | rs782608284 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chrX:154532265 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chrX:154532269 | rs72554665 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chrX:154532278 | T/T | T |
|
||
| chrX:154532279 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chrX:154532389 | rs137852324 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chrX:154532390 | rs398123546 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chrX:154532392 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chrX:154532403 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chrX:154532408 | T/T | T |
|
||
| chrX:154532411 | rs137852317 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chrX:154532432 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chrX:154532434 | rs137852337 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chrX:154532458 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chrX:154532459 | rs782098548 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chrX:154532570 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chrX:154532590 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chrX:154532608 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chrX:154532623 | T/T | T |
|
||
| chrX:154532625 | rs137852336 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chrX:154532626 | rs137852323 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chrX:154532628 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chrX:154532629 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chrX:154532634 | T/T | T |
|
||
| chrX:154532639 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chrX:154532649 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chrX:154532661 | T/T | T |
|
||
| chrX:154532662 | rs137852325 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chrX:154532667 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chrX:154532674 | rs137852335 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chrX:154532676 | rs137852316 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chrX:154532677 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chrX:154532679 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chrX:154532688 | T/T | T |
|
||
| chrX:154532692 | T/T | T |
|
||
| chrX:154532694 | rs137852321 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chrX:154532695 | rs137852334 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chrX:154532698 | rs137852320 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chrX:154532699 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chrX:154532700 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chrX:154532701 | rs137852322 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chrX:154532713 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chrX:154532715 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chrX:154532716 | T/T | T |
|
||
| chrX:154532722 | rs371489738 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chrX:154532752 | CGGCCTTGC GCTCGTTCA G/ CGGCCTTGC GCTCGTTCA G |
CGGCCTTGC GCTCGTTCA G |
|
||
| chrX:154532758 | T/T | T |
|
||
| chrX:154532765 | rs137852329 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chrX:154532772 | rs137852345 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chrX:154532773 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chrX:154532797 | rs137852333 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chrX:154532802 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chrX:154532945 | rs34193178 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chrX:154532956 | rs398123544 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chrX:154532969 | rs137852342 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chrX:154532987 | T/T | T |
|
||
| chrX:154532989 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chrX:154532990 | rs5030869 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chrX:154533004 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chrX:154533012 | CGTGGGGTC GTCCAGGTA CCCTTTG/ CGTGGGGTC GTCCAGGTA CCCTTTG |
CGTGGGGTC GTCCAGGTA CCCTTTG |
|
||
| chrX:154533016 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chrX:154533025 | rs76723693 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chrX:154533029 | rs137852347 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chrX:154533031 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chrX:154533044 | rs137852339 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chrX:154533064 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chrX:154533072 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chrX:154533077 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chrX:154533083 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chrX:154533122 | rs137852327 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chrX:154533586 | rs74575103 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chrX:154533587 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chrX:154533589 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chrX:154533591 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chrX:154533592 | T/T | T |
|
||
| chrX:154533596 | rs137852318 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chrX:154533605 | T/T | T |
|
||
| chrX:154533607 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chrX:154533608 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chrX:154533614 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chrX:154533615 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chrX:154533619 | T/T | T |
|
||
| chrX:154533620 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chrX:154533629 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chrX:154533634 | rs137852346 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chrX:154534036 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chrX:154534074 | TCAGTGC/ TCAGTGC |
TCAGTGC |
|
||
| chrX:154534092 | T/T | T |
|
||
| chrX:154534102 | rs782757170 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chrX:154534110 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chrX:154534116 | ATGT/ATGT | ATGT |
|
||
| chrX:154534125 | rs137852328 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chrX:154534126 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chrX:154534157 | rs137852319 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chrX:154534345 | rs137852326 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chrX:154534348 | rs782754619 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chrX:154534387 | rs781865768 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chrX:154534389 | rs137852332 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chrX:154534390 | rs137852330 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chrX:154534409 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chrX:154534414 | GGGA/GGGA | GGGA |
|
||
| chrX:154534419 | rs5030868 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chrX:154534438 | rs267606836 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chrX:154534440 | rs5030872 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chrX:154534447 | T/T | T |
|
||
| chrX:154534455 | T/T | T |
|
||
| chrX:154534463 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chrX:154534465 | rs137852343 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chrX:154534468 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chrX:154534485 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chrX:154534486 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chrX:154534489 | rs137852331 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chrX:154534494 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chrX:154534495 | rs137852314 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chrX:154535176 | rs370918918 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chrX:154535180 | rs782487723 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chrX:154535187 | rs137852313 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chrX:154535190 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chrX:154535211 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chrX:154535244 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chrX:154535247 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chrX:154535249 | rs782322505 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chrX:154535261 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chrX:154535269 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chrX:154535270 | rs78365220 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chrX:154535274 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chrX:154535277 | rs1050829 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chrX:154535278 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chrX:154535301 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chrX:154535316 | rs5030870 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chrX:154535330 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chrX:154535336 | rs267606835 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chrX:154535342 | rs181277621 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chrX:154535367 | GCTT/GCTT | GCTT |
|
||
| chrX:154535379 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chrX:154535962 | rs782308266 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chrX:154535963 | rs138687036 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chrX:154535980 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chrX:154535995 | rs782090947 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chrX:154535996 | rs137852349 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chrX:154536002 | rs1050828 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chrX:154536008 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chrX:154536019 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chrX:154536021 | CAGA/CAGA | CAGA |
|
||
| chrX:154536025 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chrX:154536032 | rs137852315 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chrX:154536034 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chrX:154536035 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chrX:154536045 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chrX:154536151 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chrX:154536156 | rs76645461 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chrX:154536168 | rs78478128 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chrX:154536169 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chrX:154546045 | rs137852338 | CATG/CATG | CATG |
|
|
| chrX:154546046 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chrX:154546057 | T/T | T |
|
||
| chrX:154546061 | rs137852340 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chrX:154546116 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chrX:154546122 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chrX:154546131 | G/G | G |
|
HLA-B allele match data
| Allele Reported: | *15:02/*57:01 |
|---|
IFNL3/4 allele match data
| Allele Matched: | rs12979860 reference (C)/rs12979860 reference (C) |
|---|---|
| Phasing Status: |
Unphased PharmCAT reports the genotype(s) that receive the highest score during the matcher process. In case of unphased data, additional genotypes might be possible and cannot be ruled out. |
Calls at Positions
| Position in VCF | RSID | Call in VCF | Reference | Related Alleles and Function | Warnings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| chr19:39248147 | rs12979860 | C/C | C |
|
MT-RNR1 allele match data
| Variant Reported: | 1555A>G |
|---|
NUDT15 allele match data
| Allele Matched: | *1/*1 |
|---|---|
| Phasing Status: |
Unphased PharmCAT reports the genotype(s) that receive the highest score during the matcher process. In case of unphased data, additional genotypes might be possible and cannot be ruled out. |
Calls at Positions
| Position in VCF | RSID | Call in VCF | Reference | Related Alleles and Function | Warnings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| chr13:48037748 | rs769369441 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr13:48037749 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chr13:48037782 | rs746071566 | AGGAGTC/ AGGAGTC |
AGGAGTC |
|
|
| chr13:48037798 | rs186364861 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr13:48037825 | rs777311140 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr13:48037834 | rs1202487323 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr13:48037847 | rs766023281 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr13:48037849 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chr13:48037885 | rs1950545307 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr13:48037902 | rs149436418 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr13:48040977 | rs1457579126 | GA/GA | GA |
|
|
| chr13:48041103 | rs761191455 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr13:48041113 | rs1368252918 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr13:48045690 | rs768324690 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr13:48045714 | rs1185228044 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr13:48045719 | rs116855232 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr13:48045720 | rs147390019 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr13:48045771 | rs139551410 | T/T | T |
|
RYR1 allele match data
| Allele Matched: | Reference/Reference |
|---|---|
| Phasing Status: |
Unphased |
Calls at Positions
| Position in VCF | RSID | Call in VCF | Reference | Related Alleles and Function | Warnings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| chr19:38433867 | rs193922744 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:38440747 | rs193922745 | CGAT/CGAT | CGAT |
|
|
| chr19:38440796 | rs193922746 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:38440802 | rs193922747 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:38440818 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chr19:38440829 | rs193922748 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38440830 | rs139161723 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38440851 | rs193922749 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38442361 | rs118192160 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38442373 | rs995399438 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:38442395 | rs118192113 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38442434 | rs186983396 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38443790 | rs142474192 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38444179 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chr19:38444187 | rs193922750 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38444191 | rs193922751 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38444203 | rs193922752 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:38444211 | rs118192161 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38444212 | rs193922753 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38444217 | rs193922754 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38444220 | rs193922755 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38444221 | rs193922756 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:38444250 | rs761616815 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38444252 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chr19:38444253 | rs193922757 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38444257 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chr19:38444671 | rs771058055 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38446481 | rs727504129 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38446492 | rs193922759 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38446517 | rs112596687 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:38446520 | rs193922760 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:38446710 | rs1801086 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38448500 | rs752652072 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38448501 | rs193922761 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38448673 | rs193922762 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38448680 | T/T | T |
|
||
| chr19:38448712 | rs121918592 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38448715 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chr19:38448791 | rs113332073 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38451785 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chr19:38451842 | rs193922764 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38451843 | rs193922766 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38451850 | rs118192116 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38452985 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chr19:38452996 | rs193922767 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38455247 | rs147723844 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:38455253 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chr19:38455254 | T/T | T |
|
||
| chr19:38455269 | rs901087791 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38455347 | T/T | T |
|
||
| chr19:38455359 | rs118192162 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:38455463 | rs111888148 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38455471 | rs193922768 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38455472 | rs144336148 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38455489 | rs193922769 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:38455504 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chr19:38455528 | rs193922770 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38457539 | rs118204423 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38457545 | rs118192172 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38457546 | rs193922772 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38458175 | rs747177274 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38458247 | rs138874610 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38460461 | rs376149732 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38460551 | rs193922775 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38463499 | rs370634440 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38464649 | rs148623597 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38466144 | rs778241277 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38466216 | rs180714609 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38466315 | rs141942845 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38466347 | rs111272095 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38466386 | rs2145447772 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38466392 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chr19:38467655 | rs749040743 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38469002 | rs193922776 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38469111 | rs549201486 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38469404 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chr19:38469415 | rs936513262 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38473635 | rs34694816 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:38475335 | rs137933390 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:38477816 | rs145573319 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:38483293 | rs146429605 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:38483329 | rs754476250 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38483345 | rs151029675 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38483357 | rs193922777 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38485679 | T/T | T |
|
||
| chr19:38485688 | rs781104539 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:38485691 | rs146504767 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38485787 | rs754785770 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:38485838 | rs193922781 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38485841 | rs193922782 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:38485972 | rs192863857 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38485996 | rs372958050 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:38486015 | rs34934920 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38486095 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chr19:38486096 | rs193922783 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:38490151 | rs145801146 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38490642 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chr19:38492540 | rs35364374 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38494379 | rs746818096 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:38494381 | rs770593660 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38494426 | rs193922788 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38494454 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chr19:38494464 | rs117886618 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38494465 | rs193922789 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38494555 | rs143398211 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38494564 | rs118192175 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38494565 | rs118192163 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38494579 | rs118192176 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38494621 | rs193922790 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:38494625 | rs959170123 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38496265 | rs193922791 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38496278 | rs141646642 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38496283 | rs118192177 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38496294 | rs193922792 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38496301 | rs193922793 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:38496306 | rs193922795 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38496415 | rs199870223 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38496416 | rs537994744 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38496455 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chr19:38496487 | rs763352221 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38496488 | rs140152019 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38496502 | rs917523269 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38496901 | rs193922797 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38496910 | rs118192121 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:38499177 | rs34390345 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:38499223 | rs112563513 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38499234 | T/T | T |
|
||
| chr19:38499241 | rs147213895 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:38499639 | rs193922798 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38499642 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chr19:38499643 | rs193922799 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38499644 | rs121918596 | TGGA/TGGA | TGGA |
|
|
| chr19:38499650 | rs193922801 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:38499655 | rs193922802 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38499667 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chr19:38499670 | rs193922803 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38499680 | T/T | T |
|
||
| chr19:38499682 | rs769482889 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38499683 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chr19:38499691 | rs762401851 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38499692 | rs193922804 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:38499696 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chr19:38499697 | rs193922805 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:38499704 | rs193922806 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38499706 | rs146306934 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38499719 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chr19:38499730 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chr19:38499731 | rs193922807 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38499806 | rs976108591 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:38499817 | rs111364296 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38499975 | rs193922809 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38499984 | rs193922810 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38499985 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chr19:38499993 | rs121918593 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38499997 | rs28933396 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38500000 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chr19:38500003 | rs193922812 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38500010 | rs193922813 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38500636 | rs118192124 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38500637 | rs193922815 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38500640 | rs118192123 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:38500642 | rs193922816 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38500643 | rs118192122 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38500654 | rs28933397 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38500655 | rs121918594 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38500667 | rs551223467 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38500863 | rs193922817 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38500898 | rs118192178 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38500899 | rs193922818 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38500904 | rs193922819 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:38502652 | rs767553612 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:38502663 | rs193922822 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38502669 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chr19:38502670 | rs751180702 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38502679 | rs193922824 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38502708 | rs748575133 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:38502923 | rs914804033 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38504298 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chr19:38504319 | rs193922826 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38504347 | rs781126470 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38504868 | rs193922827 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38504869 | rs112196644 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:38504878 | rs193922828 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38505061 | rs193922829 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38505325 | rs147707463 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38505358 | rs35180584 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38505923 | rs193922830 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38505932 | rs768535909 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:38506361 | rs193922831 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:38506492 | rs112772310 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38506508 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chr19:38506865 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chr19:38507821 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chr19:38511590 | rs147303895 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38512279 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chr19:38512321 | rs193922832 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38512367 | rs193922833 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38515052 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chr19:38516167 | rs199738299 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:38516181 | T/T | T |
|
||
| chr19:38516184 | rs553055844 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38516208 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chr19:38517431 | rs375626634 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:38517470 | T/T | T |
|
||
| chr19:38517521 | rs757753317 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38517523 | T/T | T |
|
||
| chr19:38517541 | rs112151058 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38519237 | rs118204421 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38519238 | rs193922834 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38519292 | rs137932199 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38519295 | rs118192126 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:38519424 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chr19:38519432 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chr19:38519447 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chr19:38525432 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chr19:38525492 | rs143987857 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38527707 | rs55876273 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38527710 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chr19:38528372 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chr19:38529002 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chr19:38529036 | rs193922838 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38529042 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chr19:38529048 | rs375915752 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38534726 | rs4802584 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38534774 | rs763112609 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38534775 | rs193922839 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38535197 | rs111565359 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38535998 | rs140616359 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38543365 | rs148399313 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38543380 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chr19:38543405 | rs193922840 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:38543551 | rs147136339 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:38543566 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chr19:38543810 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chr19:38543816 | rs118204422 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:38543821 | rs193922842 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38543832 | rs193922843 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38546460 | rs755088027 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38546496 | rs773040531 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:38548253 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chr19:38548259 | rs144685735 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38548287 | rs193922844 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38548380 | rs373406011 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38561140 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chr19:38561185 | rs193922848 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:38561213 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chr19:38561228 | rs201321695 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:38561236 | rs193922849 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38561243 | rs193922850 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:38561362 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chr19:38561363 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chr19:38561383 | rs151119428 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38565023 | T/T | T |
|
||
| chr19:38565034 | rs193922852 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38565182 | rs193922853 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:38565215 | rs587784372 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38565218 | rs193922855 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38566978 | rs139647387 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:38566986 | rs150396398 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38570619 | rs771741606 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38570620 | rs118192130 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38570649 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chr19:38572032 | rs143520367 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38572185 | rs118192135 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38572190 | rs756850145 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:38572206 | rs193922860 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38572262 | rs759500310 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:38572266 | rs193922862 | TC/TC | TC |
|
|
| chr19:38573180 | rs193922863 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38573229 | rs193922864 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:38573304 | rs118192140 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38575957 | rs200766617 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38577931 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chr19:38577942 | rs193922865 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:38577946 | rs193922866 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38577954 | rs193922867 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38577955 | rs193922868 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38578015 | rs768360593 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38578205 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chr19:38580004 | rs118192167 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:38580039 | TT/TT | TT |
|
||
| chr19:38580041 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chr19:38580066 | rs143988412 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:38580075 | rs193922873 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38580088 | rs193922874 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:38580094 | rs121918595 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38580114 | rs193922876 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38580126 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chr19:38580370 | rs193922878 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38580382 | rs193922879 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38580397 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chr19:38580403 | rs118192168 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38580416 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chr19:38580425 | rs193922880 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38580439 | rs118192181 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38580440 | rs63749869 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38580485 | rs113210953 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr19:38580497 | rs193922883 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:38584974 | rs118192151 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38584976 | rs193922888 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38584989 | rs118192170 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:38585078 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chr19:38585099 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chr19:38585947 | rs111657878 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:38585948 | rs118192159 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38585951 | rs193922895 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38585952 | rs118192158 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38585959 | rs193922896 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr19:38586101 | rs193922898 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr19:38586140 | rs146876145 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr19:38586190 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chr19:38587362 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chr19:38587363 | G/G | G |
|
SLCO1B1 allele match data
| Allele Matched: | *1/*1 |
|---|---|
| Phasing Status: |
Unphased PharmCAT reports the genotype(s) that receive the highest score during the matcher process. In case of unphased data, additional genotypes might be possible and cannot be ruled out. |
In case no genotype can be determined, recommendations are based on the rs4149056 genotype alone as per guideline. The minor C allele at rs4149056 defines SLCO1B1*5.
Calls at Positions
| Position in VCF | RSID | Call in VCF | Reference | Related Alleles and Function | Warnings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| chr12:21172734 | rs139257324 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr12:21172776 | rs373327528 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr12:21172782 | rs56101265 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr12:21174595 | rs56061388 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr12:21176804 | rs2306283 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr12:21176868 | rs2306282 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr12:21176871 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chr12:21176879 | rs11045819 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr12:21176883 | rs72559745 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr12:21176898 | rs77271279 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr12:21178612 | rs141467543 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr12:21178615 | rs4149056 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr12:21178957 | rs79135870 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr12:21196951 | rs11045852 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr12:21196975 | rs183501729 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr12:21196976 | rs11045853 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr12:21200544 | rs72559747 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr12:21200595 | rs55901008 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr12:21202553 | rs1228465562 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr12:21202555 | rs59113707 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr12:21202649 | rs56387224 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr12:21202664 | rs142965323 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr12:21205921 | rs72559748 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr12:21205999 | rs59502379 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr12:21206031 | rs74064213 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr12:21222355 | rs71581941 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr12:21239042 | rs34671512 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr12:21239077 | rs56199088 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr12:21239113 | rs55737008 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr12:21239145 | rs200995543 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr12:21239158 | rs140790673 | C/C | C |
|
TPMT allele match data
| Allele Matched: | *1/*1 |
|---|---|
| Phasing Status: |
Unphased PharmCAT reports the genotype(s) that receive the highest score during the matcher process. In case of unphased data, additional genotypes might be possible and cannot be ruled out. |
Calls at Positions
| Position in VCF | RSID | Call in VCF | Reference | Related Alleles and Function | Warnings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| chr6:18130687 | rs1142345 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr6:18130694 | rs150900439 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr6:18130725 | rs72552736 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr6:18130729 | rs139392616 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr6:18130758 | rs398122996 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr6:18130762 | rs56161402 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr6:18130772 | rs377085266 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr6:18130781 | rs1800584 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr6:18132136 | rs72556347 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr6:18132147 | rs79901429 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr6:18132163 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chr6:18133845 | rs75543815 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr6:18133847 | rs6921269 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr6:18133870 | rs772832951 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr6:18133884 | rs74423290 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr6:18133887 | rs201695576 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr6:18133890 | rs9333570 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr6:18138969 | rs144041067 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr6:18138970 | rs112339338 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr6:18138997 | rs1800460 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr6:18139027 | rs72552737 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr6:18139689 | rs72552738 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr6:18139710 | rs200220210 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr6:18143597 | T/T | T |
|
||
| chr6:18143606 | rs151149760 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr6:18143613 | C/C | C |
|
||
| chr6:18143622 | rs115106679 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr6:18143643 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chr6:18143700 | rs753545734 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr6:18143718 | rs111901354 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr6:18143724 | rs1800462 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr6:18143728 | rs1256618794 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr6:18147838 | rs281874771 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr6:18147845 | rs777686348 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr6:18147851 | rs200591577 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr6:18147856 | A/A | A |
|
||
| chr6:18147910 | rs72552740 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr6:18149004 | G/G | G |
|
||
| chr6:18149022 | rs750424422 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr6:18149032 | rs759836180 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr6:18149045 | rs72552742 | T/T | T |
|
|
| chr6:18149126 | rs267607275 | A/A | A |
|
|
| chr6:18149127 | rs9333569 | T/T | T |
|
UGT1A1 allele match data
| Allele Matched: | *1/*1 |
|---|---|
| Phasing Status: |
Unphased PharmCAT reports the genotype(s) that receive the highest score during the matcher process. In case of unphased data, additional genotypes might be possible and cannot be ruled out. |
Calls at Positions
| Position in VCF | RSID | Call in VCF | Reference | Related Alleles and Function | Warnings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| chr2:233759924 | rs887829 | C/C | C |
|
|
| chr2:233760233 | rs3064744 | CAT/CAT | CAT |
|
|
| chr2:233760498 | rs4148323 | G/G | G |
|
|
| chr2:233760973 | rs35350960 | C/C | C |
|
VKORC1 allele match data
| Variant Matched: | rs9923231 reference (C)/rs9923231 reference (C) |
|---|---|
| Phasing Status: |
Unphased PharmCAT reports the genotype(s) that receive the highest score during the matcher process. In case of unphased data, additional genotypes might be possible and cannot be ruled out. |
Calls at Positions
| Position in VCF | RSID | Call in VCF | Reference | Related Alleles and Function | Warnings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| chr16:31096368 | rs9923231 | C/C | C |
|
Disclaimers and Other Information
Liability: PharmCAT assumes no responsibility for any injury to person or damage to persons or property arising out of, or related to any use of PharmCAT, or for any errors or omissions. The user recognizes that PharmCAT is a research tool and that they are using PharmCAT at their own risk.
A. Allele and Genotype Determination
PharmCAT uses gene allele definitions included in the CPIC database, with exceptions as noted in Gene Definition Exceptions document. For allele definitions and the positions used in PharmCAT, see the gene definition tables.
Genes with DPWG recommendations that are not included in CPIC are discussed in Section C.
PharmCAT results are dependent on the supplied VCF calls for the queried positions (for technical information about PharmCAT input formatting and requirements, please go to pharmcat.org). PharmCAT does not assume any reference calls for positions missing from the submitted VCF file; all missing queried positions are not considered in the allele determination process. See the pharmcat_positions file for which positions are queried in the VCF file. Missing positions might alter the assigned genotype and subsequent phenotype prediction and CPIC recommendation. If the supplied VCF file has missing positions, those positions will be noted in Section III: Allele Matching Details for each gene of this report. For the most reliable allele determination, reference calls as well as variant calls in the VCF file for every queried position must be provided by the user. If an allele that includes a missing position is defined by an additional position(s) for which calls are provided, the allele will be considered in the matching process based on the available information. This might lead to the output of multiple possible genotypes that received the same highest matching score. In addition, alternate calls with a lower score is also possible. For instructions on getting PharmCAT to output all possible matching genotypes, consult the documentation.
For cytochrome P450 genes, TPMT, NUDT15, UGT1A1, and SLCO1B1, the *1 allele is defined by the absence of variation specified in the gene definition tables. This allele cannot be identified by variants; rather, *1 is assigned by default when no variation for the queried positions is reported in the submitted VCF file. The same is true for all other genes with multiple variant positions in the definition table (CACNA1S, CFTR, DPYD, RYR1): the reference sequence is the default result when variants are not reported in the VCF file. It is always possible un-interrogated variation can occur which could potentially affect allele function, but because it is undetected, the assignment would be defaulted to a *1 (or reference) allele and normal function.
For all genes, variation reported in the VCF file but NOT included in the gene definition table will not be considered during allele assignment. There is a possibility that any such variation results in a reduced or no activity allele which could lead to inaccurate phenotype and CPIC recommendation, similar to the situation in point 3, above.
Nucleotide base calls are displayed on the positive chromosomal strand regardless of the gene strand; further information is provided under Gene-specific warnings in Section III: Allele Matching Details.
Structural variation star alleles that cannot be detected using VCF file data:
- CYP2B7-CYP2B6 hybrids: CYP2B6*29, CYP2B6*30
- Partial and whole gene deletions: CYP2C19*36, CYP2C19*37, CYP4F2*16, SLCO1B1*48, SLCO1B1*49
PharmCAT matches variants to genotypes assuming unphased data (unless phased data is provided in the VCF file and noted as such, see pharmcat.org for details). The assumption is that defined alleles exist in trans configuration, i.e. on opposite chromosomes, with exceptions noted in Section III: Allele Matching Details under "Gene-specific warnings." However, in cases where an allele is defined by a combination of two or more variants, where each variant alone also defines an allele, the match is based on the longer allele. For example, TPMT*3B is defined by one SNP, *3C is defined by another SNP, and *3A is defined by the combination of those two SNPs. In the case of unphased data that is heterozygous for both SNPs, the *1/*3A genotype is returned though the possibility of *3B/*3C cannot be ruled out.
Below cases are summarized for which two calls with different scores are possible when provided unphased data and heterozygous calls for the variants that define the two alleles. The genotype with the higher score (longer allele) will be used to determine allele functionality, phenotype, and recommendation but the genotype with the lower score cannot be ruled out.
Table 1: Cases for which there is an overlap in the allele definitions.
| Gene | Genotype (Higher Score) | Phenotype | Genotype (Lower Score) | Phenotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UGT1A1 | *1/*80+*28 | Intermediate | *28/*80 | Indeterminate |
| UGT1A1 | *1/*80+*37 | Intermediate | *37/*80 | Indeterminate |
| TPMT | *1/*3A | Intermediate | *3B/*3C | Poor |
| NUDT15 | *1/*2 | Intermediate | *3/*6 | Possible Intermediate |
| CYP2C9 | *1/*71 | N/A | *10/*22 | Indeterminate |
| CYP2B6 | *1/*36 | Intermediate | *6/*22 | Intermediate |
| CYP2B6 | *1/*34 | Intermediate | *33/*36 | Indeterminate |
| CYP2B6 | *1/*6 | Intermediate | *4/*9 | Intermediate |
| CYP2B6 | *1/*7 | Intermediate | *5/*6 | Intermediate |
| CYP2B6 | *1/*13 | Intermediate | *6/*8 | Intermediate |
| SLCO1B1 | *1/*46 | Decreased function | *15/*45 | Possible Decreased Function |
| SLCO1B1 | *1/*20 | Normal Function | *19/*37 | Indeterminate |
| SLCO1B1 | *1/*12 | Indeterminate | *2/*10 | Indeterminate |
| SLCO1B1 | *1/*13 | Indeterminate | *3/*11 | Indeterminate |
| SLCO1B1 | *1/*14 | Normal Function | *4/*37 | Indeterminate |
| SLCO1B1 | *1/*15 | Decreased function | *5/*37 | Decreased function |
| SLCO1B1 | *1/*25 | Indeterminate | *4/*28 | Indeterminate |
| SLCO1B1 | *1/*31 | Decreased function | *9/*37 | Decreased Function |
| SLCO1B1 | *1/*32 | Indeterminate | *4/*24 | Indeterminate |
| SLCO1B1 | *1/*40 | Indeterminate | *5/*19 | Possible Decreased Function |
| SLCO1B1 | *1/*43 | Indeterminate | *4/*44 | Indeterminate |
| CYP4F2 | *1/*4 | N/A | *2/*3 | N/A |
| CYP3A4 | *1/*37 | N/A | *3/*22 | N/A |
| CYP3A4 | *1/*38 | N/A | *3/*11 | N/A |
| G6PD | A- 202A_376G/B (reference) | Variable | A/Asahi | Variable |
| G6PD | B (reference)/Mt Sinai | Variable | A/Guadalajara | Variable |
| G6PD | B (reference)/Santa Maria | Variable | A/Malaga | Variable |
| G6PD | Ananindeua/B (reference) | Variable | A/Viangchan, Jammu | Variable |
| G6PD | B (reference)/Hechi | Variable | Asahi/Viangchan, Jammu | Deficient |
| G6PD | B (reference)/Hermoupolis | Variable | Cassano/Union,Maewo, Chinese-2, Kalo | Deficient |
Table 2: Cases for which there is an overlap in the allele definitions because the definition of the non-*1 allele in the genotype with the higher score allows for reference or variant at the position that defines the first allele listed in the genotype with the lower score. Both genotypes cannot be ruled out with unphased data if the position that overlaps between the respective alleles is heterozygous (0/1) in addition to heterozygous calls for the other variants that define the non-*1 allele in the genotype with the higher score.
| Gene | Genotype (Higher Score) | Phenotype | Genotype (Lower Score) | Phenotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CYP2C19 | *1/*4 | Intermediate | *17/*4 | Intermediate |
| CYP2C19 | *1/*2 | Intermediate | *11/*2 | Intermediate |
| CYP2C19 | *1/*35 | Intermediate | *15/*35 | Intermediate |
| CYP2B6 | *1/*18 | Intermediate | *4/*18 | Indeterminate |
B. CPIC Allele Function, Phenotype and Recommendation
All content is sourced from the CPIC database.
C. DPWG Allele Function, Phenotype and Recommendation
PharmGKB annotates PGx-based drug dosing guidelines published by the Royal Dutch Association for the Advancement of Pharmacy - Pharmacogenetics Working Group (DPWG). PharmGKB curates allele function assignments and phenotype mappings from the DPWG to provide genotype specific DPWG guideline recommendations. Where possible, PharmGKB maps DPWG terms to CPIC terms, as outlined on PharmGKB.
CYP3A4 is currently not part of a CPIC guideline. Since the DPWG CYP3A4 documentation includes limit variant notations for the included alleles (only *16, *20, and *22 are specified) PharmCAT relies on PharmVar CYP3A4 allele definitions. However, the CYP3A4*16, *20 and *22 definitions are the same in both sources.
The CPIC UGT1A1 allele definition file includes *6, *27, *28, *36, *37, and *80. Since the DPWG UGT1A1 document does not include allele definitions besides for the UGT1A1 TA box promoter polymorphism, PharmCAT only includes the UGT1A1 positions from the CPIC UGT1A1 allele definition file. Other UGT1A1 alleles can be supplied as outside calls but not be determined from the VCF file by the Named Allele Matcher.
D. FDA drug-label and Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations recommendations
PharmCAT includes recommendations from PharmGKB-annotated FDA drug labels and the FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations. It only contains FDA information for genes with CPIC or DPWG guidelines because the FDA does not offer any genotype-to-phenotype mapping information. PharmCAT uses CPIC genotype-to-phenotype mappings when they exist, and DPWG genotype-to-phenotype mappings when no CPIC mappings exist, to determine the phenotypes to use with FDA label annotations and Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations entries. Results presented for FDA Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations use wording and “Affected Subgroups” taken directly from the Table. Results presented from PharmGKB-annotated drug labels present wording from the specific label that was curated. In many cases, multiple FDA labels may exist for a particular medication. Typically, PharmGKB annotates the label linked to from the FDA Table of Pharmacogenomic Biomarkers in Drug Labeling but in some cases a different label may be annotated. Follow the “FDA Label Annotation” link in section II of the report to access the annotated label and more information.
E. Source Tags in Section II
Part of PharmGKB’s annotations of guidelines, drug labels and Table of Pharmacogenetic Associations is the assignment of labels that are meant to provide a high-level indication of the provided action. If recommendations or FDA Table wording exists, yellow boxes display if the guidance/wording is regarding (1) a dosing change, (2) recommending an alternate drug be used, or (3) other guidance. These boxes are included in the Source column in Section II of the PharmCAT report. More detailed information about what the yellow boxes mean is available on PharmGKB.
F. PharmCAT Exceptions to the CPIC Guideline Gene List
PharmCAT does not determine CYP2D6, MT-RNR1, HLA-A, or HLA-B genotypes from the VCF file, but genotypes for CYP2D6, MT-RNR1, HLA-A, or HLA-B can be provided to PharmCAT from an outside source and the corresponding phenotype prescribing recommendations will be included in the generated report. For the required format of the outside calls refer to the PharmCAT outside calls documentation.
CPIC has assigned function to the following CYP2D6 CNV alleles: *1x2, *1x≥3, *2x2, *2x≥3, *3x2, *4x2, *4x≥3, *6x2, *9x2, *10x2, *17x2, *29x2, *35x2, *36x2, *41x2, *41x3, *43x2, *45x2, *146x2. These alleles are part of the CPIC diplotype to phenotype translation and can be connected to recommendations. Other CNV notations from outside calls need to be mapped accordingly.
G. CPIC Guideline Disclaimers and Caveats
A version of the following quoted disclaimer is part of each CPIC guideline and applies to the CPIC recommendations as used in PharmCAT. For the full description of potential benefits and risks, additional considerations (general and specific to gene-drug pairs), limitations, information about respective gene nomenclature systems, potential drug-drug interactions and clinical factors to consider, please see individual CPIC guidelines at (cpicpgx.org).
"CPIC guidelines reflect expert consensus based on clinical evidence and peer-reviewed literature available at the time they are written and are intended only to assist clinicians in decision-making and to identify questions for further research. New evidence may have emerged since the time a guideline was submitted for publication. Guidelines are limited in scope and are not applicable to interventions or diseases not specifically identified. Guidelines do not account for all individual variations among patients and cannot be considered inclusive of all proper methods of care or exclusive of other treatments. It remains the responsibility of the health-care provider to determine the best course of treatment for a patient. Adherence to any guidelines is voluntary, with the ultimate determination regarding its application to be made solely by the clinician and the patient. CPIC assumes no responsibility for any injury to persons or damage to persons or property arising out of or related to any use of CPIC's guidelines, or for any errors or omissions." (PMID: 27997040)
"Caveats: appropriate use and/or potential misuse of genetic tests. The application of genotype-based dosing is most appropriate when initiating therapy with a tricyclic. Obtaining a pharmacogenetic test after months of drug therapy may be less helpful in some instances, as the drug dose may have already been adjusted based on plasma concentrations, response, or side effects. Similar to all diagnostic tests, genetic tests are one of several pieces of clinical information that should be considered before initiating drug therapy." (PMID: 27997040)
CPIC guidelines reflect the alleles/genotypes known and considered by the guideline authors for inclusion by the time of publication, however they may be updated online at cpicpgx.org and in the CPIC database in between publications. Additional alleles and/or more extensive allele definitions might exist by the representative gene nomenclatures for various genes.
CPIC is a registered service mark of the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services (HHS).
H. PharmGKB Disclaimers and Caveats
PharmGKB is a registered service mark of the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services (HHS).